With the help of the Tibet air shower array, scientists recorded atmospheric showers of particles generated by photons hit with energies above 100 teraelectronvolts, which arrived from the Crab nebula. Recorded events were the first example of such high-energy quanta of light from a known source, and not as part of cosmic rays, the origin of which in most cases is not fully established, the authors write in the article accepted for publication in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Particles arriving from space constantly collide with the atmosphere of the Earth. It can be both fundamental and composite particles of different nature, generated by various sources (for example, the Sun) and possessing energy from a huge range. Usually, the most high-energy events relate to cosmic rays – particle flows coming from all directions. In most cases, their source cannot be detected, but individual identifications were, including with supernovae and active galactic nuclei.
When interacting with atomic nuclei in the upper layers of the atmosphere, such particles generate a cascade of reactions, which leads to the appearance of a large number of secondary particles — an atmospheric shower. Some of them reach the surface of the Earth and can be registered. Since the initial impact occurs at a high altitude, the “fragments” generated by one high-energy particle can cover an area of hundreds of square kilometers.
One of the most intense known sources of particles is the Crab Nebula – the supernova remnant of 1054, inside which there is a pulsar. In particular, it detects electromagnetic radiation from radio to an extremely hard gamma range with a maximum energy of several tens of teraelectronvolts.
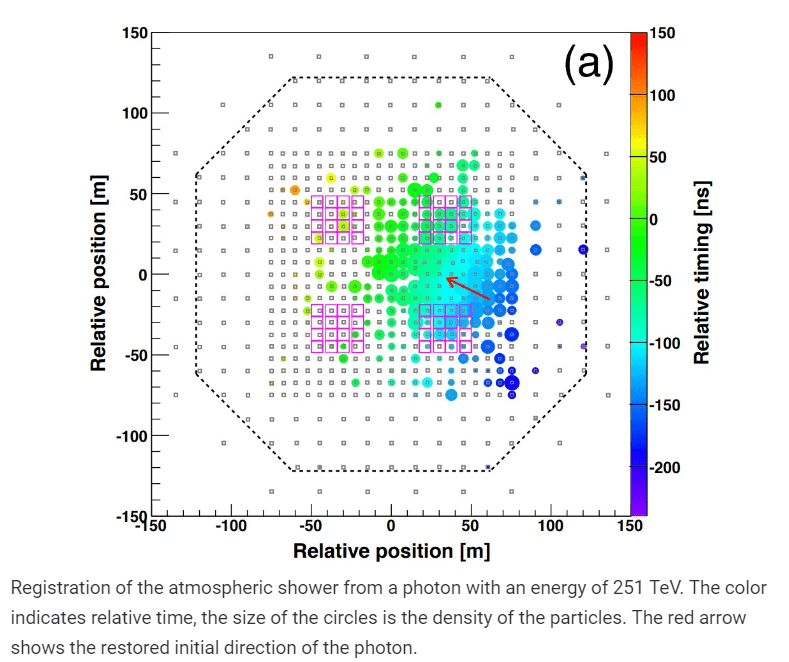
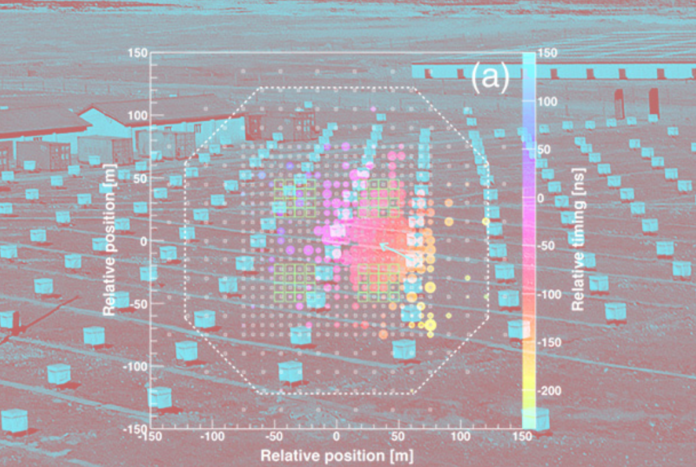
The collaboration of scientists working with the Tibet air shower array installation describes the first case of photon fixation with an energy above 100 teraelectronvolts from a particular source, which was the Crab Nebula. After taking into account all sources of noise, physicists obtained 24 registrations with an expected number of background events from cosmic rays of 5.5, which corresponds to a statistical significance of 5.6σ. Among them, in four cases, the energy exceeded even 250 teraelectronvolts with an expected amount of 0.8 (statistical significance 2.4σ).
The registration was carried out using ground-based scintillation detectors and underground muon detectors, which capture the Cherenkov radiation of secondary muons. At the moment, such detectors installation Tibet air shower array have a total area of 3400 square meters. The distinction between photons and massive particles of cosmic rays was made by the number of generated muons – a photon of comparable energy generates much less muons.
This year, observations began on the most sensitive cosmic ray detector, also located in China. Last year, for the first time, we managed to find a source of ultrahigh-energy neutrinos, which turned out to be a blazar. Cosmic rays affect not only the Earth, but also other bodies: recently scientists proved that the color of the satellite of Jupiter of Europe is determined, among other things, by high-energy particles.