Pneumococcal disease causes millions of hospitalizations and hundreds of thousands of deaths every year.
A recent study by Carlos J. Orihuela and colleagues, published in the open-access journal PLOS Biology, suggests that the FDA-approved drug Fomepizole could alleviate disease severity in mice with certain forms of bacterial pneumonia while improving the efficacy of erythromycin, an antibiotic.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the primary cause of community-acquired pneumonia, and current vaccines are ineffective against certain multidrug-resistant strains.
The limited treatment options for antibiotic-resistant S. pneumoniae infections prompted the researchers to conduct experiments with mice, which demonstrated that Fomepizole, when combined with antibiotics, reduced the bacterial burden in the lungs and prevented invasive disease.
To assess the efficacy of novel treatments for antibiotic-resistant S. pneumoniae, the scientists conducted experiments on mice. They administered fomepizole, an FDA-approved drug used to treat toxic alcohol ingestion, to mice infected with multidrug-resistant S. pneumoniae, along with antibiotics.
Fomepizole inhibits the enzyme alcohol dehydrogenase, blocking normal energy production by the bacteria and enhancing their susceptibility to antibiotics. The researchers compared the bacterial burden in the infected organs of the experimental group to that of the control group.
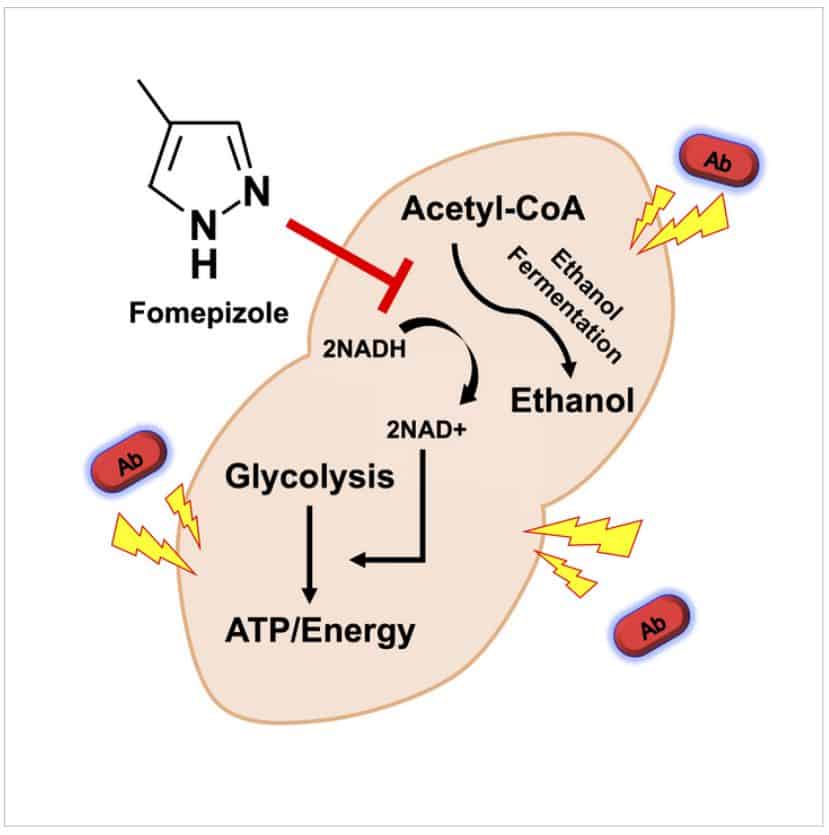
The study found that the combination treatment reduced bacterial burden in the lungs of mice with pneumonia and prevented the development of invasive disease. While promising, this novel drug treatment has not yet been tested in clinical studies on humans, who may present with complicating factors that could affect the outcome of the treatment.
However, further research is necessary to assess the treatment’s effectiveness in human patients, considering potential complicating factors such as comorbidities and environmental variables.
Orihuela notes that “pharmacological targeting of fermentation pathways is a new way to enhance the susceptibility of some bacteria to antimicrobials. Combination treatment of erythromycin and fomepizole, an alcohol dehydrogenase inhibitor, prevented the in vivo dissemination of antibiotic-resistant Streptococcus pneumoniae.”
Source: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3002020
Image Credit: Getty
