Scientists at the NIH shed light on how the structure of genes affects gene expression, tissue-specific function, and the way a disease appears.
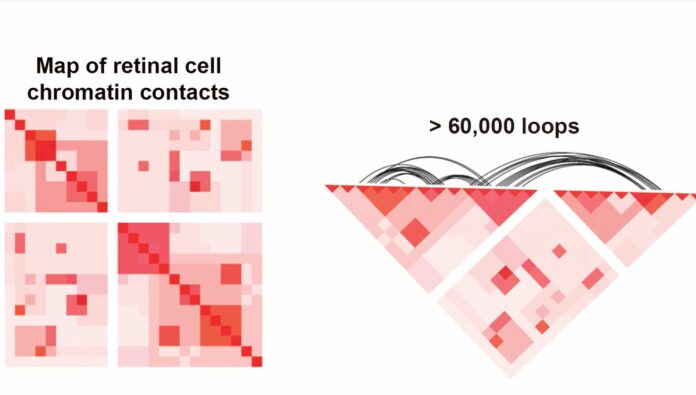
Scientists at the National Eye Institute created a map of how human retinal cell chromatin is organized. Chromatin is made up of fibers that pack 3 billion nucleotide-long DNA molecules into small structures that fit into chromosomes in the nucleus of each cell.
The complete gene regulatory network that was made as a result shows how gene expression is controlled in general and how the retina works in both rare and common eye diseases. The findings appeared in the journal Nature Communications.
“This is the first detailed integration of retinal regulatory genome topology with genetic variants associated with age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and glaucoma, two leading causes of vision loss and blindness,” adds lead investigator, Anand Swaroop.
Adult human retinal cells are highly specialized sensory neurons that do not divide and are thus relatively stable for studying how the three-dimensional structure of chromatin influences genetic information expression.
Chromatin fibers wrap long strands of DNA around histone proteins and loop them repeatedly to form very compact structures.
All of these loops produce several sites of contact where protein-coding genetic sequences interact with gene regulatory regions such as super enhancers, promoters, and transcription factors.
Such non-coding sequences have been dubbed “junk DNA” for a long time. However, more advanced studies show how these sequences influence which genes are transcribed and when, offering details on the specific processes by which non-coding regulatory elements exert control even when they are located on a different DNA strand from the genes they regulate.
Using deep Hi-C sequencing, a technique for examining 3D genome architecture, the researchers generated a high-resolution map of retinal cell chromatin with 704 million contact sites.
Post-mortem retinal samples from four human donors were used to create the maps.
The researchers then combined the chromatin topology map with gene and regulatory element databases.
What surfaced was a dynamic picture of interactions within chromatin throughout time, including regions with variable degrees of isolation from other DNA regions and hotspots for gene activity.
They discovered unique patterns of interaction at retinal genes, pointing to how chromatin’s 3D architecture is crucial for the regulation of genes in particular tissues.
“Having such a high-resolution picture of genomic architecture will continue to provide insights into the genetic control of tissue-specific functions,” Swaroop adds.
In addition, similarities between mouse and human chromatin organization show conservation across species, highlighting the significance of chromatin organizing patterns for retinal gene regulation.
In the human retina, 35.7% of gene pairs that interacted through a chromatin loop in mice also did so.
The chromatin topological map was combined with information on gene variants linked to AMD and glaucoma, two of the most common conditions that result in vision loss and blindness, as determined by data from genome-wide association studies. The results identify particular possible causative genes that are connected to those disorders.
The integrated genome regulatory map will also help in assessing genes linked to other prevalent retina-related conditions, such as diabetic retinopathy, figuring out missing heritability, and comprehending genotype-phenotype relationships in inherited retinal and macular illnesses.
NEI Intramural Research Program Funds ZIAEY000450 and ZIAEY000546 sponsored the research.
Source: 10.1038/s41467-022-33427-1
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: NIH Creates First Detailed 3D Map Of Human Retinal Cell Chromatin