According to this new study, scientists have created thin films of glass-shaped aluminium oxide, which can be stretched, compressed and bent without cracks at room temperature. These properties allow the creation of fragile glass, but the technology of producing large-scale products from this material does not yet exist.
Glass is an amorphous solid, that is, not having a crystalline structure. Many substances can form materials with this structure, but silica-based glasses are the most common option. Such glasses are characterized by transparency and hardness, but also fragility, that is, the inability to deform without cracks.
The properties of glass, especially its thermal and chemical durability, provided it with a large number of applications. However, in many cases, fragility becomes a problem: for example, it cracks the screens of smartphones. Researchers are constantly trying to improve the indicators of glass, but so far they are far from predicted by the theory.
The reason lies in the microscopic structure of glass – it looks like a disordered distribution of silicon and oxygen atoms with small voids playing the role of defects. If the mechanical energy is not used for reversible elastic or irreversible plastic deformation, it will accumulate near defects. In a normal glass, atoms cannot shift, tearing old and forming new connections with others, which is used energy, so the result is a crack and glass breaks.
A team of scientists led by Erkka Frakenberg from the University of Tampere in Finland investigated thin glass films composed of alumina Al 2 O 3. It turned out that such material is capable of plastic stretching and compressing without cracking if it was initially free from defects. Researchers compare the behaviour of the resulting substance with metals that ordinary glass does not look like.
The authors received a new glass through pulsed laser spraying, that is, evaporation of the original crystalline substance followed by deposition on the substrate. In particular, they could be stretched by 8 per cent, compressed in half and bend. These changes were plastic, meaning the material did not take its original form after the external exposure was removed.
To clarify the reasons for these properties, scientists examined the obtained samples using an electron microscope. A computer model based on the obtained data showed that, first of all, a defect-free structure with dense packing of atoms was responsible for this. Also, in such a glass, atoms could be displaced by external action.
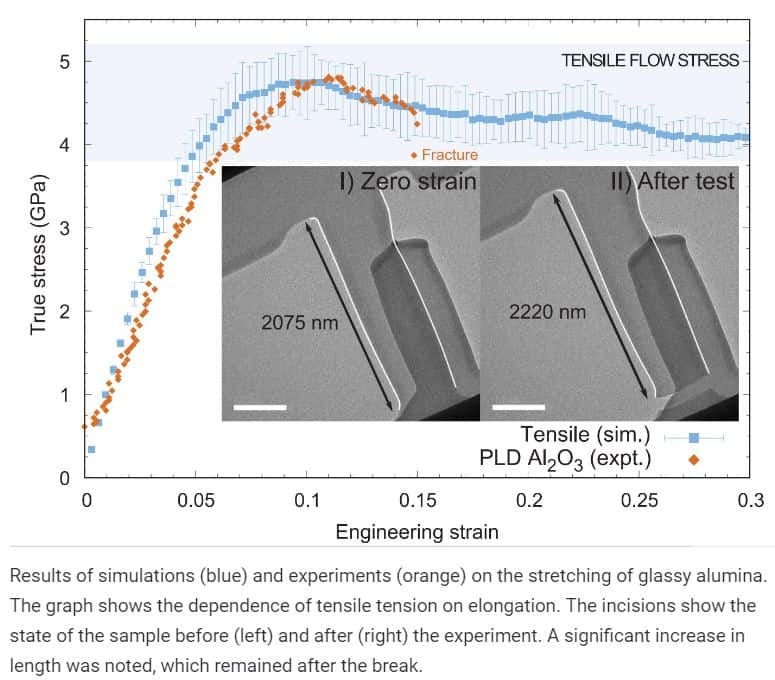
Scientists note that the results demonstrate the possibility of using plastic glass films made of aluminium oxide today. For example, such products can be useful in the production of batteries and electronics. Potentially there may be other applications, but it is necessary to learn to create large products with the right properties, and this way the authors can not offer yet.
