The find sheds light on the mysterious nature of glass and its state transitions.
An interdisciplinary team of German physicists claims to have found an additional state of matter. Its particles behave in a way never seen before. The group had been suggesting that it had existed for 20 years.
Although in everyday life we often use the words glass and crystal as synonyms, the truth is that they are different materials. Glass is truly present in everything we use every day, but it also hides an important scientific enigma: despite appearing to be solid, its particles do not have a crystalline structure.
- Does This Mean We Stopped Being Animal and Started Being Human Due to ‘Copy Paste’ Errors?
- The One Lifestyle Choice That Could Reduce Your Heart Disease Risk By More Than 22%
- Aging: This Is What Happens Inside Your Body Right After Exercise
- Immune-Boosting Drink that Mimics Fasting to Reduce Fat – Scientists ‘Were Surprised’ By New Findings
- Gun Violence in America: What They Don’t Talk About at the Debate
Normally, when matter goes from a liquid to a solid state, its molecules line up to form a crystal pattern. Instead, the glass particles freeze in place before crystallization occurs. The nature of this strange and disorderly state remains a mystery and scientists are still trying to understand the chemical and physical properties that characterize it.
Liquid glass, a new state of matter
The multidisciplinary team of scientists from the Department of Chemistry, at the University of Konstanz in Germany, claims to have discovered a transitory state of matter, dubbed liquid glass.
It appears to be a state present between the solid and the colloidal phase. The latter is nothing more than a dispersion of matter made up of two or more phases, normally one fluid (liquid or gas) and the other dispersed in the form of very fine solid particles. An example of a colloidal system could be foam or a gel.
To date, most experiments involving colloidal suspensions have been based on spherical colloids – or particles. But the team led by Professors Andreas Zumbusch and Matthias Fuchs realized that deformed colloids abound in nature. As a result, they manufactured small plastic particles, stretching and cooling them until they achieved their ellipsoid shapes and then placed them in a suitable solvent.
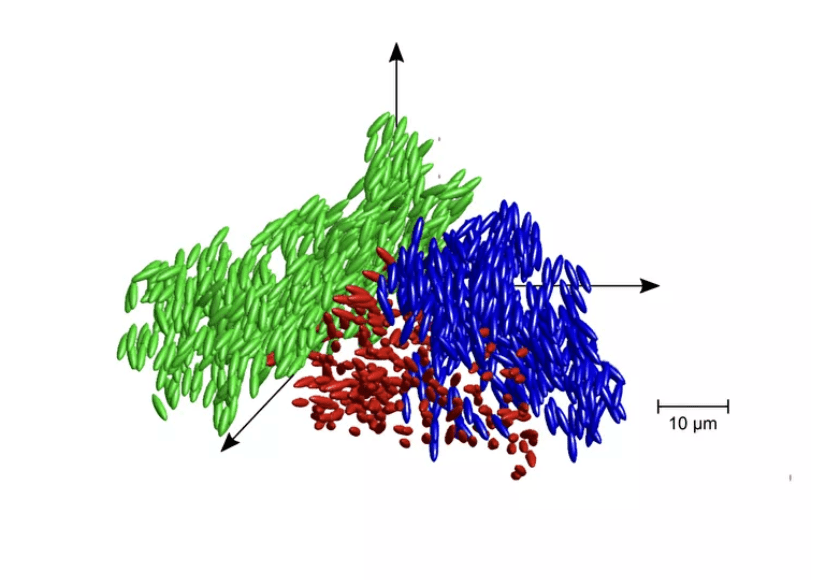
© PHOTO: ANDREAS ZUMBUSCH AND MATTHIAS FUCHS RESEARCH GROUP
“Because of their distinctive shape, our particles are oriented – unlike spherical particles – leading to completely new and previously unstudied kinds of complex behavior,” says study co-author Andreas Zumbusch, professor of physical chemistry at the University of Konstanz.
What researchers have called liquid glass is the result of clusters of these elliptical colloids obstructing each other, so that they can move but not rotate. Thus, the particles obtain more flexibility than glass molecules, but not enough to compare them with regular materials that have already been extensively studied.
This represents a complex type of particle behavior that has not been previously observed in laboratories. Furthermore, the shape and concentration of the particles appear to play a crucial role in the creation of the liquid glass, the German researchers suggest.
Matthias Fuchs, professor of condensed soft matter theory at the University of Konstanz, explains why the project is relevant.
“This is incredibly interesting from a theoretical point of view. Our experiments provide a type of evidence for the interaction between critical fluctuations and crystal structure that the scientific community has been looking for for quite some time.”
For the past 20 years, the existence of liquid glass had been the subject of speculation. Now, the results of their discovery have been published in the journal of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States (PNAS).
The scientists suggest that their discovery may help shed light on the behavior of complex systems and molecules ranging from the very small (biological) to the very large (cosmological). Furthermore, it could also have an impact on the development of liquid crystal devices, such as our monitors.
