New Findings Indicate Like Earth Liquid Water Still Exists On Mars
The latest data from an international research team suggests that there may be liquid water beneath Mars’ south polar ice cap.
The team, led by the University of Cambridge, used satellite laser-altimeter readings of the upper surface of the ice cap to find tiny patterns in its height. They then demonstrated that the predicted effects of water beneath the ice cap on the surface are consistent with these patterns.
Their findings are consistent with prior ice-penetrating radar readings, which were initially believed to indicate the possibility of a liquid water area beneath the ice. Some studies have cast doubt on the liquid water interpretation from the radar data alone, claiming that the radar signal is not caused by liquid water.
The findings, which were published in the journal Nature Astronomy, offer the first line of independent proof that liquid water exists beneath Mars’ south polar ice cap using the information other than radar.
“The combination of the new topographic evidence, our computer model results, and the radar data,” said lead author professor Neil Arnold, “make it much more likely that at least one area of subglacial liquid water exists on Mars today, and that Mars must still be geothermally active in order to keep the water beneath the ice cap liquid.”
Water ice caps exist at both poles of Mars, and their combined volume is nearly the same as Earth’s Greenland Ice Sheet. The polar ice caps on Mars, on the other hand, have until recently been assumed to be frozen solid all the way to their beds due to the cold Martian temperature, unlike Earth’s ice sheets, which are underlain by water-filled channels and even vast subglacial lakes.
This notion was refuted in 2018 by data gathered by the European Space Agency’s Mars Express mission. The satellite contains a MARSIS ice-penetrating radar that can see through the southern ice cap of Mars. It showed that there was a place at the bottom of the ice that strongly reflected the radar signal. This was thought to be a place where water was still liquid under the ice cap.
But later studies showed that other types of dry materials on Mars that aren’t under the ice cap could make similar patterns of reflectance if they are there. Given the frigid climate, liquid water beneath the ice cap would need a different heat source, such as geothermal heat from within the planet, at temperatures higher than those anticipated for the Martian climate at the time. This meant that confirmation of the lake’s existence needed to come from a different source.
On Earth, subglacial lakes have an impact on the surface topography of the ice sheet that lies above them. Ice flow under gravity is influenced by the water in subglacial lakes because it reduces friction between the ice sheet and its bed. This, in turn, changes the shape of the ice sheet surface above the lake, often making a depression in the ice surface followed by a raised area further down-flow.
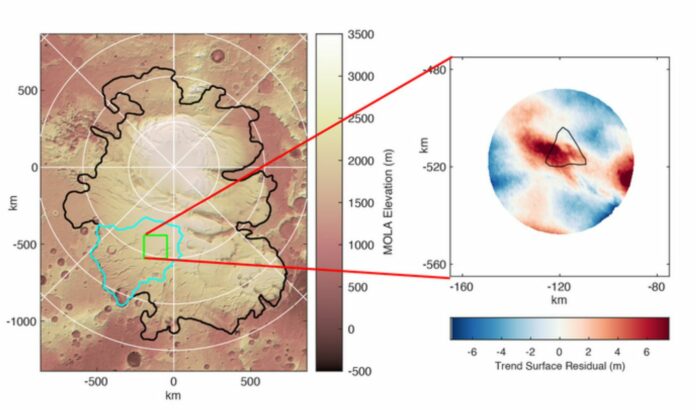
The team, which also included academics from the Universities of Sheffield, Nantes, University College, and Dublin, examined data from NASA’s Mars Global Surveyor satellite about the surface topography of the region of Mars’ south polar ice cap where the radar signal was detected using a range of approaches.
According to their investigation, there is a surface undulation that is between 10 and 15 kilometers long and consists of a depression and a corresponding raised area that are both several meters away from the surrounding ice surface. The size of this is comparable to the undulations above subglacial lakes on Earth.
The team then tried to figure out if the waves they saw on the ice’s surface could be caused by liquid water at the bed. They performed ice flow computer simulations that were tailored to the unique Martian environment. Then, they added a region of reduced bed friction where, in the case of real water, the ice would be able to slide and accelerate. They also manipulated the amount of heat generated from the planet’s interior, known as geothermal heat. The ripples on the surface of the simulated ice were the same size and shape as the ones the team saw on the surface of the real ice cap.
There may be an accumulation of liquid water beneath Mars’ south polar ice cap, and magmatic activity in the planet’s subsurface only recently enabled the enhanced geothermal heating required to maintain the water in a liquid state, according to the similarity between topographic undulation produced by models and actual spacecraft observations.
“The quality of data coming back from Mars, from orbital satellites as well as from the landers, is such that we can use it answer really difficult questions about conditions on, and even under the planet’s surface, using the same techniques we also use on Earth,” added Arnold. “It’s exciting to use these techniques to find out things about planets other than our own.”
Source: 10.1038/s41550-022-01782-0
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: “At Least One Area Of Subglacial Liquid Water Exists On Mars Today” – New Data