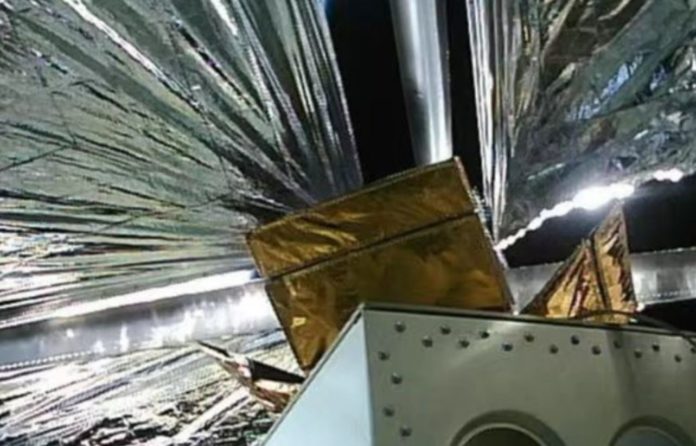
China has made new progress in cleaning up space junk by successfully putting a 25-square-meter deorbiting sail on the payload capsule of a recently launched rocket.
According to the architects of the technology, who spoke to the Global Times on Tuesday, this was the first time a deorbiting sail system has ever been deployed in this way.
The deorbiting sail device, created by Institute 805 of the Shanghai Academy of Spacecraft Technology (SAST), is intended to reduce the spread of space garbage and junk by allowing malfunctioning spacecraft to exit orbit sooner.
The sail was attached to the Long March-2D Y64 carrier rocket’s cargo module before it was sent into orbit on June 23. According to the SAST, the system was successfully unfolded in orbit on June 26.
According to the SAST developers, the sail system has a 25 square meter surface area and can allow a 300 kilogram cargo capsule to re-enter the Earth’s atmosphere in two years, freeing up valuable orbital resources.
The developers also stated that the size of the deorbiting sail set a record.
The sail’s thickness is less than one tenth of the width of a hair, and it is comprised of extremely thin materials. The SAST claims that because the sail system is so light and extensible, it can be mounted on any advanced spacecraft.
The SAST described the deorbiting sail device to the Global Times as a giant space kite that, once deployed, can aid in slowing down spacecraft.
The SAST stated that the thin sail employs aerodynamic resistance created by the thin atmosphere of the low-orbit environment to progressively decelerate the satellite and gradually exit the original orbit.
If no deorbiting steps are implemented, a small satellite with an orbit altitude of 750 kilometers and a weight of 15 kilograms can continue to operate in orbit for 120 years or even longer beyond the end of its operational life. The 2,25-square-meter deorbiting sail can cut satellites’ deorbiting period to less than 10 years.
In September 2019, China conducted its first test of a comparable passive deorbiting 2.25-square-meter deorbiting sail device known as Taurus.
Space debris poses a threat to missions in orbit. The most common instance is the collision between the US “Iridium 33” and the Soviet Union’s decommissioned “Cosmos-2251” at a distance of about 800 kilometers above Siberia.
In addition to taking out Iridium 33, the crash also created a significant amount of debris that was dispersed over more than a thousand kilometers in space and had a significant impact on later space initiatives.
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: China Just Deployed Its Deorbiting Sail in Space