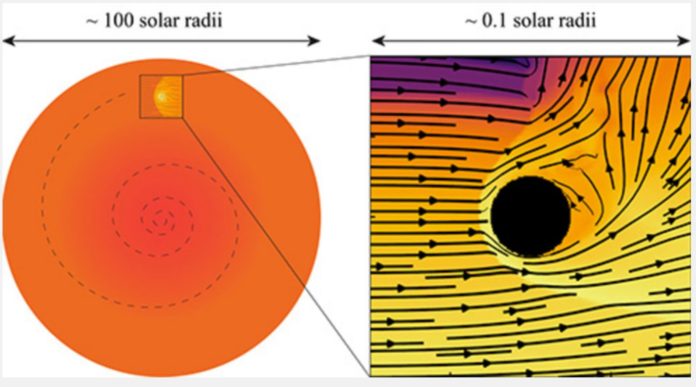
When the hydrogen fuel in our sun’s core runs out in 5 billion years, it will expand into a red giant, engulfing the inner planets. Planetary engulfment’s mechanics and various outcomes are unknown, but it is assumed to be a fairly typical fate for planetary systems.
New research employing hydrodynamic simulations illustrates the forces exerted on a planet by an expanding star. The findings reveal that interactions between a substellar body (a planet or brown dwarf) and the hot gas of a sun-like star’s outer envelope can result in a variety of consequences depending on the size of the swallowed object and the stage of the star’s growth.
The new discoveries will be presented by lead author Ricardo Yarza of the University of California, Santa Cruz, at the 240th meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS) in Pasadena today.
“Evolved stars can be hundreds or even thousands of times larger than their planets,” says Yarza, a UCSC graduate student in astronomy and astrophysics, “and this disparity of scales makes it difficult to perform simulations that accurately model the physical processes occurring at each scale.” “Instead, we simulate a small section of the star centered on the planet to understand the flow around the planet and measure the drag forces acting on it.”
The findings could explain recent sightings of planets and brown dwarfs orbiting stellar remnants like white dwarfs and subdwarfs in close proximity. Previous research has proposed that these systems are the consequence of a planetary engulfment process that entails the swallowed body’s orbit decreasing and the ejection of the star’s outer layers.
“As the planet travels inside the star, drag forces transfer energy from the planet to the star, and the stellar envelope can become unbound if the transferred energy exceeds its binding energy,” ads Yarza.
According to Yarza and his colleagues’ calculations, no substellar entities less than about 100 times Jupiter’s mass can eject a sun-like star’s envelope before it has expanded to around 10 times the radius of the sun. However, at later stages of stellar growth and expansion, an object as tiny as ten times the mass of Jupiter might eject the stellar envelope, shrinking Jupiter’s orbit by many orders of magnitude in the process.
The study also discovered that planetary engulfment can boost a sun-like star’s luminosity by many orders of magnitude for thousands of years, depending on the mass of the engulfed object and the star’s developmental stage.
This study’s approach can be used in future research to investigate the effects of engulfment on the star’s structure. “Our work can inform simulations of planetary engulfment at the scale of the star by providing an accurate reference picture of the physics at the scale of the planet,” Yarza remarks.
Exoplanet search programs have now documented a wide range of planetary systems. A considerable number of these systems are anticipated to be engulfed by the planets as they evolve. “We believe it is relatively common,” the author adds.
Image Credit: RICARDO YARZA ET AL.
You were reading: New Study Reveals Mysterious Forces Pulling Planet to Star and Also how they interact