A long time ago, photosynthesis and green leaves were regarded as essential aspects of plants. Nevertheless, some plants have subsequently stopped using this method and now get their nutrition from other living things.
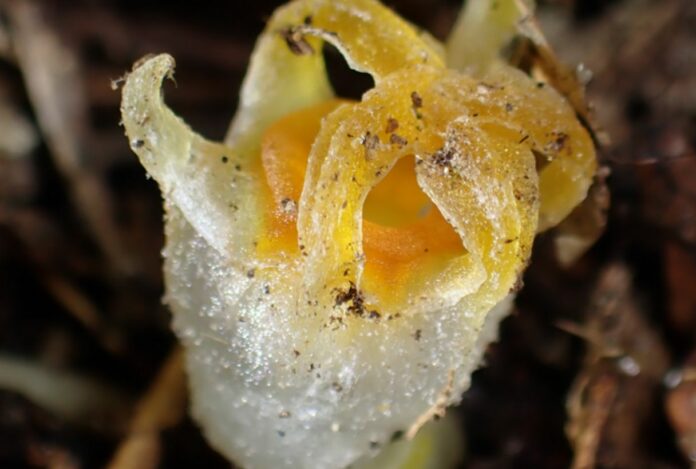
One such plant is the Thismia genus, sometimes referred to as fairy lanterns, which is distinguished by its peculiar look, enigmatic nature, and absence of photosynthesis. Fairy lanterns are uncommon and only seen in select locations.
They reside below, but their colorful blossoms rise above the dirt, giving them the appearance of mushrooms.
Over 90 Thismia species have been discovered, however many are only known from their initial finding area, and several are presumably extinct.
Thismia kobensis is one of such species, and it was first found in Kobe City, Japan, in 1992. Sadly, an industrial complex devastated its habitat, and it was later thought to be extinct.
Professor Kenji Suetsugu and his colleagues found it again after more than 30 years in Sanda City, which is about 30 km away.
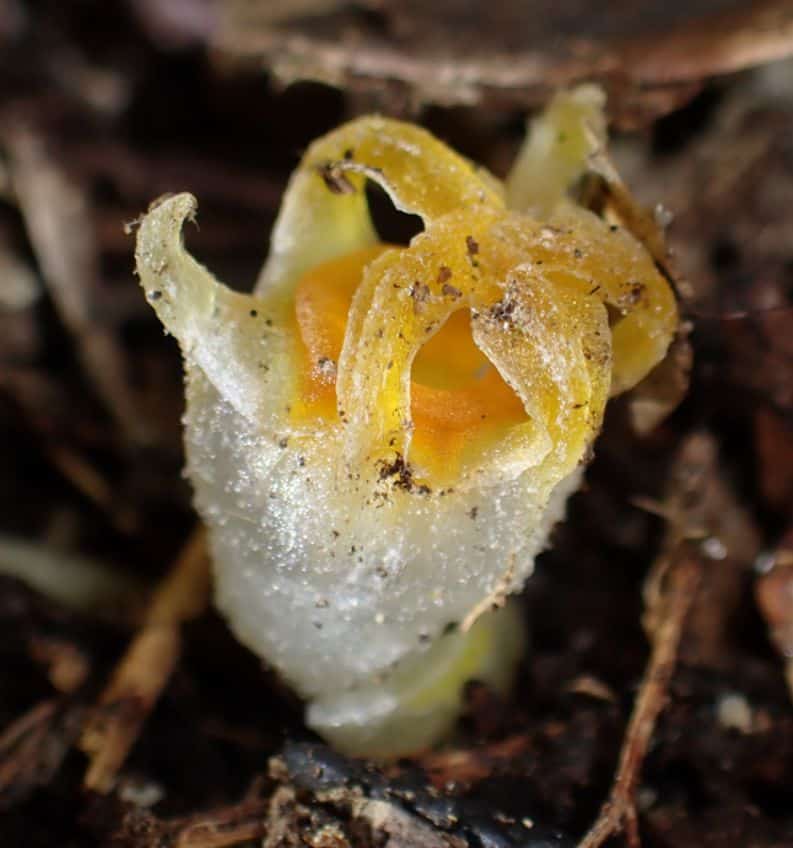

This surprise discovery and the ensuing research have revealed previously unknown details about the evolutionary history of this unique species.
In order to complete the initial description of Thismia kobensis, which had been based on a fragmented museum specimen, the researchers offered a new and more detailed description.
They focused on the differences between Thismia kobensis and Thismia huangii, a closely related species. This newly found species is easily recognizable by its small and broad ring and its dense covering of short hairs on the stigma.
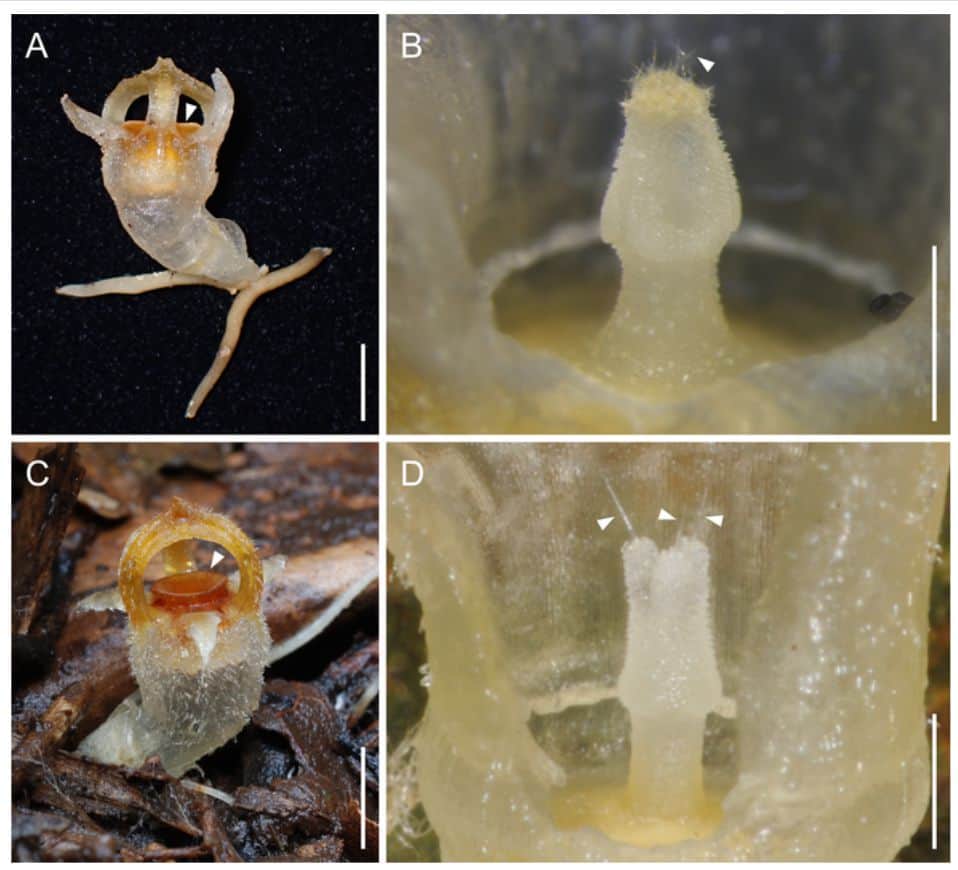

The researchers analyzed a number of traits and came to the conclusion that Thismia kobensis is a unique species with its own set of characteristics and lineage of evolution.
Thismia kobensis is the northernmost known species of Asian fairy lantern because of its recently found location. This finding may provide fresh insights on the systematic affinities and biogeography of the enigmatic fairy lantern, Thismia americana, which was previously believed to be linked to several Australian and New Zealand species.
Thismia americana, the sole species of North American fairy lantern found more than a century ago, was sighted for a few years on a grassland near Chicago, but is now thought extinct.
It is still unclear why the mostly tropical genus Thismia exists in temperate North America, particularly because Thismia rodwayi, the species thought to be its closest cousin, is only found in Australia and New Zealand. Botanists are still perplexed by this odd distribution pattern.
Nevertheless, a thorough morphological analysis indicated that Thismia kobensis is really Thismia americana’s closest cousin. In light of pollinator preferences, it is possible that Thismia americana and the species from Australia and New Zealand independently acquired comparable outer floral morphologies.
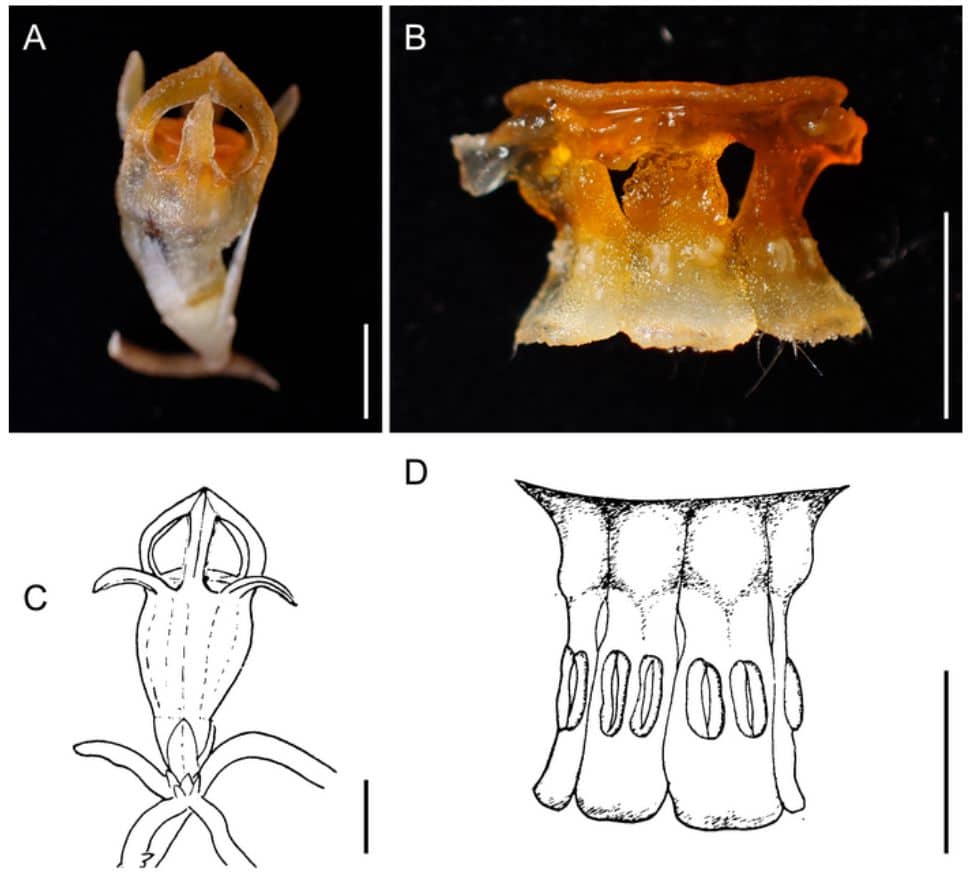
This shows that Thismia americana may not be linked to the species found in Australia and New Zealand. The significant resemblance in inner floral anatomy, on the other hand, shows a closer connection between Thismia americana and Thismia kobensis, as seen by the absence of nectar glands in both species.
It is not unusual for plant species to have close connections and disparate ranges in Eastern Asia and North America, and this is sometimes linked to migration over the Beringia land bridge. Hence, migration across Beringia may be the cause of Thismia americana’s sporadic distribution.
Overall, the finding of the Thismia kobensis again after a thirty-year absence has greatly improved our knowledge about fairy lanterns.
It also offers vital information into the biogeography and evolutionary history of fairy lanterns as a whole since it is the northernmost species of Asian fairy lantern that has been discovered so far.
The findings of the study published today in Phytotaxa.
Image Credit: Kenji Suetsugu
