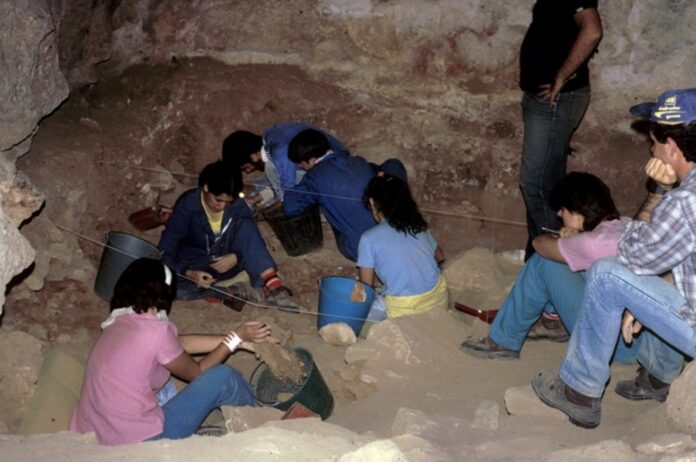
New research conducted by a CNRS researcher and published in the journal PNAS used zinc isotope analysis for the first time to figure out where Neanderthals fit in the food chain.
Based on what they found, it seems likely that they were carnivores.
Neanderthals—were they carnivores? Scientists haven’t found a clear answer yet. While some research on the dental tartar of Iberian Peninsula residents seems to indicate that they were big plant consumers, other studies conducted at locations outside of Iberia tend to suggest that they ate almost exclusively meat.
Researchers used cutting-edge analytical methods on a Neanderthal molar from the Gabasa site in Spain to conclude that the Neanderthals who lived there were likely carnivores.

Until this, scientists had to separate proteins and analyze the nitrogen isotopes present in bone collagen to determine an individual’s position in the food chain.
However, this approach is typically only applicable in temperate regions, and rarely on samples older than 50,000 years.
Nitrogen isotope analysis becomes extremely difficult or even impossible when these criteria are not satisfied. This was true of the molar from the Gabasa site that was the subject of this study’s analysis.
Given these limitations, CNRS researcher Klevia Jaouen and her team chose to examine the zinc isotope ratios found in tooth enamel, a substance that is resistant to all types of degradation.
This method has never been used before to try to figure out what a Neanderthal ate. The lower the proportions of zinc isotopes in the bones, the more likely they are to belong to a carnivore.
The same historical period and region’s animal bones, including those of carnivores like lynxes and wolves and herbivores like rabbits and chamois, were also subjected to study.
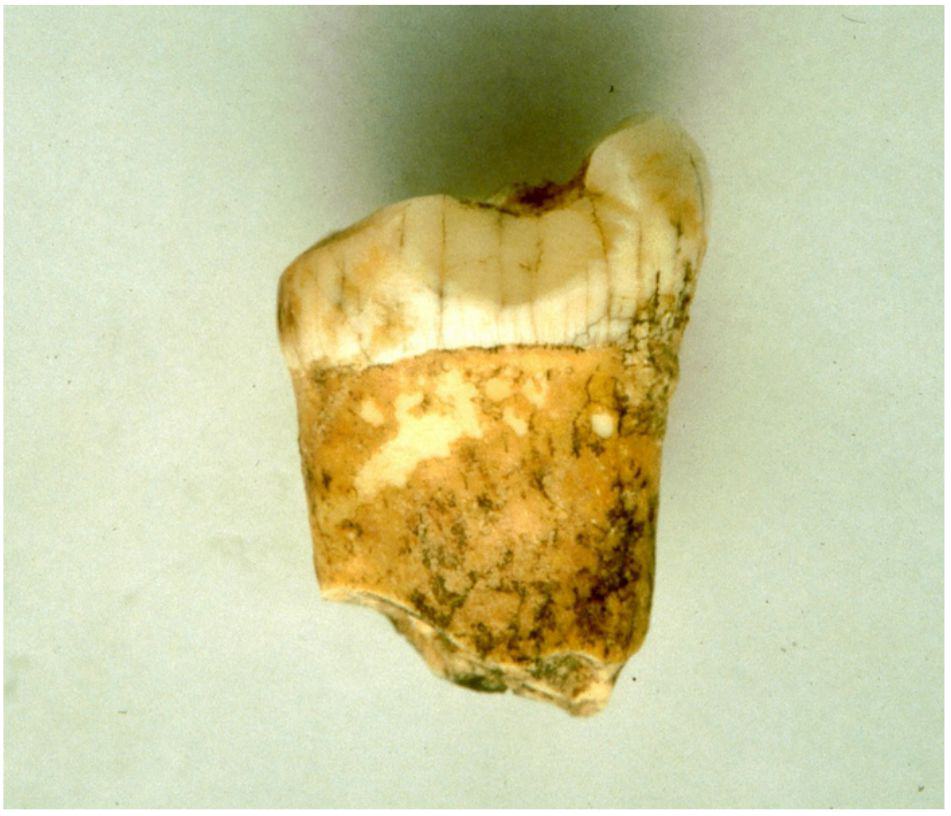
The findings show that the Neanderthal associated with this tooth from the Gabasa site was most likely a carnivore who did not consume the blood of their prey.
Broken bones discovered at the site, along with isotopic data, indicate that this individual ate the bone marrow of their prey without eating the bones, while additional chemical tracers indicate that they were weaned before the age of two.
Analyses also suggest that this Neanderthal died in the same location where they had lived as a child.
This new method of zinc isotope analysis makes it simpler to discriminate between omnivores and carnivores than prior methods.
Scientists hope to repeat the experiment on people from other sites, especially the Payre site in south-east France, where new research is being done, to make sure that their conclusions are correct.
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: Neanderthals Ate Bone Marrow Of Their Prey – Surprise Discovery Reveals
