A new study published today uncovers which fish are likely to thrive in which bodies of water, from oceans to small rivers
Fish and other aquatic creatures face a serious threat from a decrease in dissolved oxygen levels. A new study published today wants to predict which aquatic species may be threatened by changes in their habitat caused by global warming and human activity.
Larger fish are more likely to lack oxygen in warmer water than smaller ones.
The same holds true for fish with large cells, according to a new study by researchers at Radboud University. Additionally, compared to freshwater fish, marine fish are less tolerant of low oxygen levels in the ocean.
Based on these findings, the researchers want to anticipate which aquatic species may be threatened by changes in their habitat caused by global warming and human activity.
The work was just released in the journal Global Change Biology.
Fish and other aquatic species are facing a serious challenge due to declining dissolved oxygen levels.
Because of increased pollution and water heating brought on by climate change, oxygen levels are declining.
When environmental conditions change, general biological principles can help us determine which fish characteristics are advantageous or disadvantageous.
According to scientist Wilco Verberk, once these guidelines for fish have been established, “we can ultimately predict which fish species are most at risk from environmental change.”
Small and large cells
The significance of oxygen in fish susceptibility to warmer water is hotly debated among biologists.
“Many oxygen hypotheses are being fiercely debated. The problem is that the various effects are lumped together,” explains Verberk, adding “For example, some studies look at how fish respond to oxygen levels in the water but do not account for the temperature of the water or the size of the fish. As a result, the reported patterns are variable.”
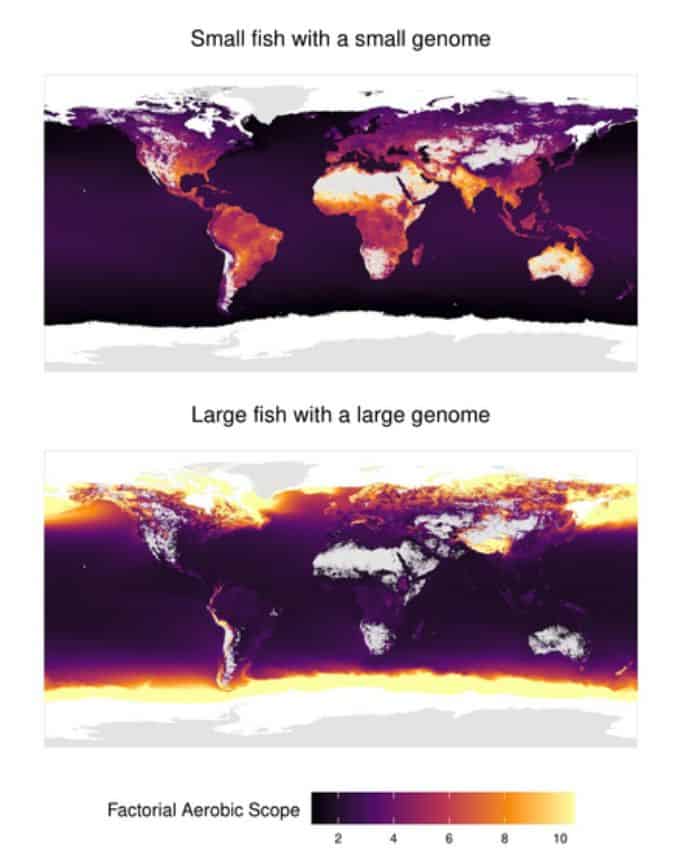
To settle this debate, Verberk and colleagues carefully isolated the various effects and accumulated information on oxygen deficiency tolerance from 195 fish species.
They discovered after analyzing the data that only in warm water do larger fishes exhibit greater sensitivity to oxygen stress. The effect is reversed when the water is cold.
For fish with comparatively large cell sizes, the researchers observed a similar result.
Many people believe that all animal species have the same cell size, however this isn’t always the case. Even within the same species, some animals have huge cells and some have small cells, according to the author.
Having small cells is helpful in many ways, especially in warm water.
“For example, small cells have relatively more membrane area, which is needed to absorb oxygen from their surrounding environment.”
Fresh, saltwater
The researchers also found differences between fish that live in fresh water and fish that live in the ocean.
“Far too often, scientific studies only compare marine and terrestrial life,” adds the author.
“Indeed, freshwater species are sometimes lumped with terrestrial species. It is a missed opportunity because taking these differences into account can greatly increase our understanding of the environmental impacts of climate change.”
Verberk and colleagues found that freshwater fishes are more tolerant to oxygen-depleted waters than marine fishes.
“The explanation probably involves different selection pressures on freshwater fish during their evolutionary history,” adds the researcher.
“In the ocean,” according to the study, “the temperature is relatively stable, but in fresh water the fish are more often confronted with higher temperatures. Fluctuations in oxygen levels are also larger in rivers and especially in lakes, for example, due to the presence of algae.”
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: Now We Know Which Fish Will Die First From Oxygen-depleted Water
