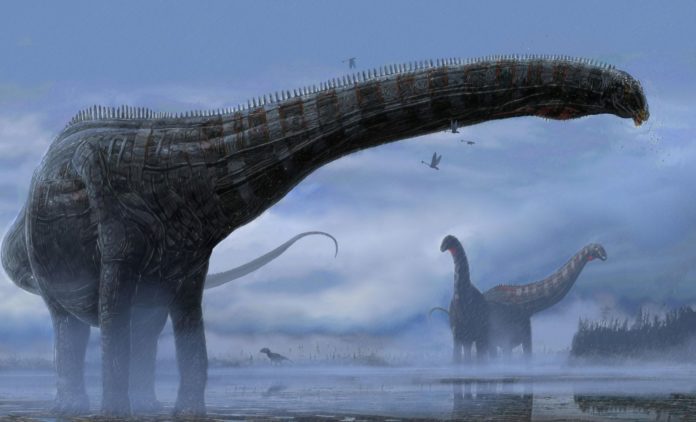
New international research says dinosaurs may have contracted and suffered from colds and respiratory infections, just like us.
According to a study published in Scientific Reports, the fossilized remains of an immature diplodocid — a huge, long-necked herbivorous sauropod dinosaur-like “Brontosaurus” – may give the first evidence of a specific respiratory disease in a dinosaur. The discoveries add to our understanding of the diseases that afflicted dinosaurs.
The “Dolly” specimen was discovered in southwest Montana, USA, and dates from the Mesozoic Era’s Late Jurassic Period (approximately 150 million years ago).

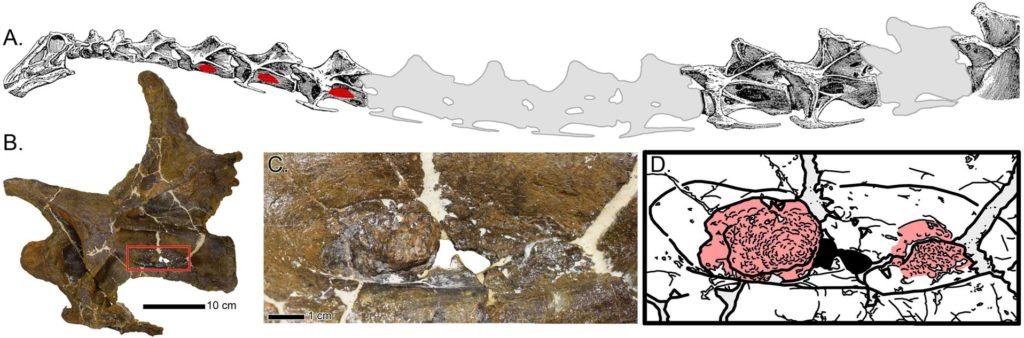
Cary Woodruff of the Great Plains Dinosaur Museum in Malta and his colleagues studied three of Dolly’s cervical vertebrae (neck bones) and discovered previously unseen aberrant bony protrusions with a peculiar shape and texture.
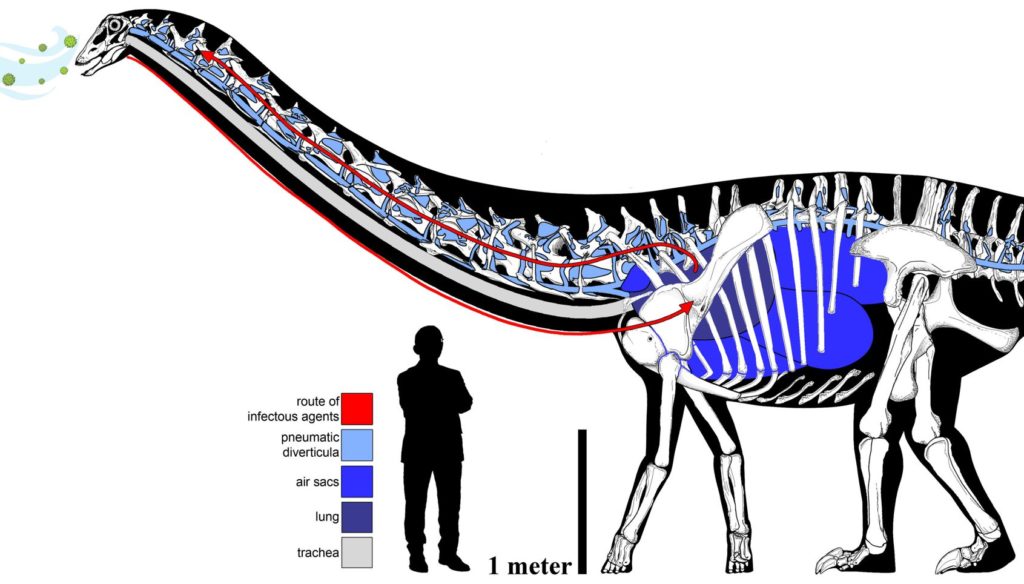
These protrusions were found at an area of each bone where air-filled sacs may have pierced them. These air sacs would have eventually connected to Dolly’s lungs, forming part of the dinosaur’s intricate respiratory system.
The uneven protrusions were found to be made of aberrant bone that had grown in response to an infection, according to CT imaging.
“Given the likely symptoms this animal suffered from, holding these infected bones in your hands, you can’t help but feel sorry for Dolly,” says Woodruff. “We’ve all experienced these same symptoms – coughing, trouble breathing, a fever, etc. – and here’s a 150-million-year-old dinosaur that likely felt as miserable as we all do when we’re sick.”
The researchers believe that these atypical bony protrusions originated in reaction to respiratory infection in Dolly, which then travelled into these neck vertebrae via the air sacs and generated the irregular bone growths.
The scientists think that a fungal infection comparable to aspergillosis, a common respiratory sickness that affects birds and reptiles today and can lead to bone infections, may have caused this respiratory infection.
This preserved infection not only documents the first occurrence of such a respiratory infection in a dinosaur but also has crucial structural implications for sauropod dinosaurs’ respiratory systems.
“This fossil infection in Dolly not only helps us trace the evolutionary history of respiratory-related diseases back in time but gives us a better understanding of what kinds of diseases dinosaurs were susceptible to,” adds Woodruff.
If Dolly had been sick with an aspergillosis-like respiratory infection, it would have displayed flu or pneumonia-like symptoms such as weight loss, coughing, fever, and breathing difficulties, according to the researchers.
They explain that because untreated aspergillosis may be lethal in birds, a potentially comparable infection in Dolly could have resulted in the animal’s death.
Source: 10.1038/s41598-022-05761-3
Image Credit: Woodruff, et al.
You were reading: Sauro-Throat? Fossilized Diplodocid Nicknamed “Dolly” found in Montana had a unique respiratory infection like us
