Based on data collected by the Cassini interplanetary station, astronomers for the first time have compiled a global geomorphological map of Saturn’s largest moon Titan, famous for its atmosphere and lakes of liquid hydrocarbons.
Titan is Saturn’s largest moon and is notable for the fact that the solar system is the only celestial body other than our planet, which has liquid lakes, rivers and seas on the surface. However, these rivers and seas consist of a mixture of methane and ethane, saturated with dissolved nitrogen. An active hydrocarbon-based hydrological cycle is responsible for the formation of one of the most interesting geological landscapes in the solar system on the surface of Titan. Despite the differences in composition, temperature and gravitational fields between Earth and Titan, many of the relief details on these two bodies may be the result of the same and those geological processes. However, for a long time the dense and opaque atmosphere of Titan prevented the study of its surface in the optical range of wavelengths, the situation changed only after arrival Saturn’s interplanetary station Cassini.
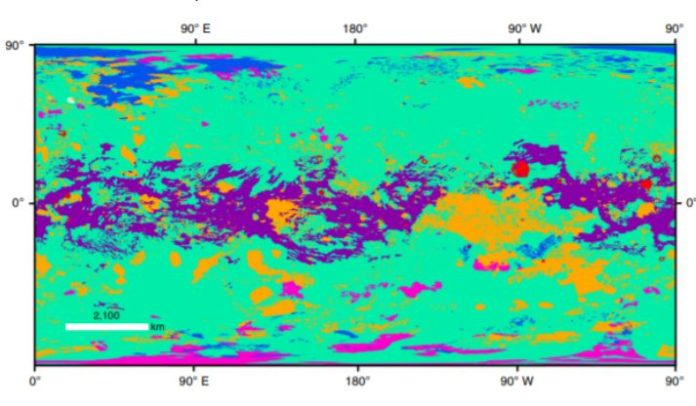
A team of Astronomers led by Rosaly Lopes reported on the results of the analysis of data obtained using the SAR radar instrument, the VIMS infrared spectrometer (Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer) and ISS (Imaging Science Subsystem). Scientists have built a global geomorphological map covering, among other things, the polar regions of Titan. Such maps allow to understand the geological evolution of celestial bodies and give information about the process of their formation.
It turned out that we can identify some of the basic geological processes that have made the surface of Titan as we see it now. This is the formation of impact craters due to the fall of meteorites, erosion of rocks under the influence of moving liquids (river) or wind (aeolian), the formation of sediments from erosion products, precipitation and dissolution of rocks, tectonic and possibly cryovolcanic activity. The geological features of Titan’s terrain depend heavily on the latitude. The youngest landscapes are dune fields, which are located in the equatorial part of the satellite, as well as lakes focused on the poles. In total, there are more than 650 lakes on Titan, dried up or filled with liquid hydrocarbons, most of them located in the northern polar region. In these areas, the rate of precipitation is greater than the rate of evaporation of liquid from the surface. At Titan’s equator, the climate is arid for long enough periods of time, which is beneficial for the formation of aeolian deposits and dunes. The dunes cover 17% of the total surface area of Titan.
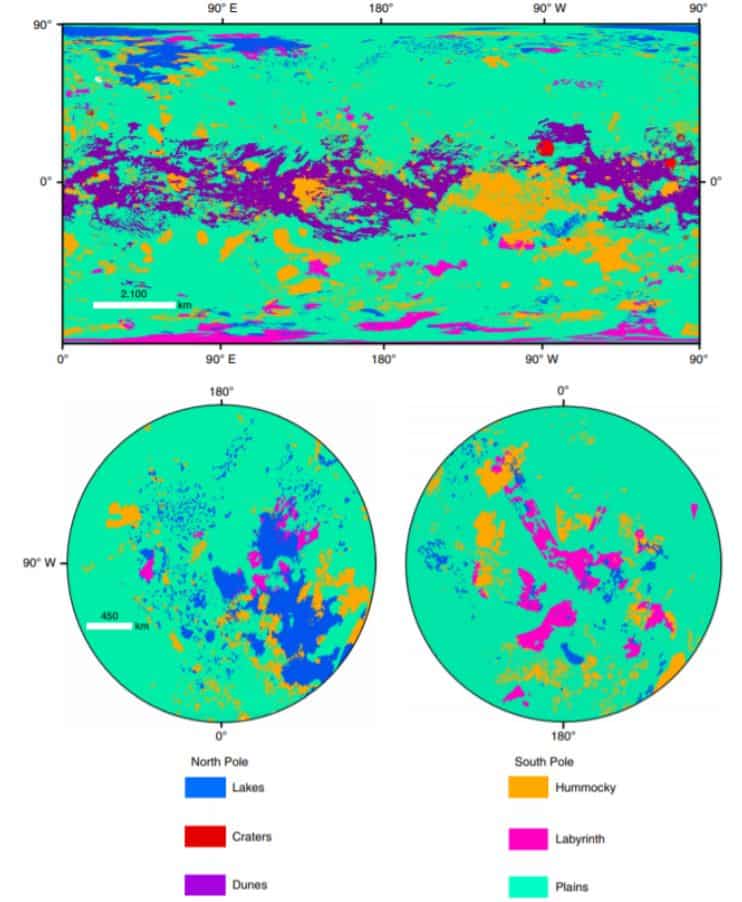
As for impact craters, they occupy only 0.4% of the total surface area of Titan. Only 23 craters with a diameter of more than twenty kilometres were found with a high degree of confidence, and several smaller candidates were found in addition. This suggests that the lifespan of the crater in Titan is several hundred million years (otherwise there would be much more). The oldest craters are near the equator, and the youngest are near the poles, where such geomorphological structures are virtually non-existent, which scientists associate with increased erosion of the surface. Mountains (both chains and single peaks) occupy 14% of Titan’s total area. They are several to tens of kilometres long and up to several kilometres high, relatively flat and consist of a material with a high content of water ice. The largest proportion of Titan’s surface area (65 per cent) is occupied by plains covered with material containing organic matter that looks almost homogeneous and has no expressed relief.