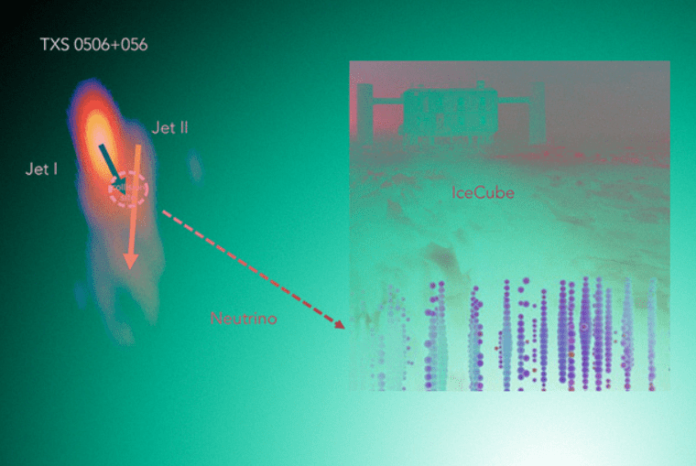
Astrophysicists have identified features in the structure of the TX-0506 + 056 blazar jet, the only identified extragalactic source of neutrinos. It turned out that the relativistic jet in this object is strongly curved and precesses, which may be due to collisions of matter ejected from the center of the galaxy. These properties make blazar atypical and may be responsible for the observed neutrino outburst.
On July 12, 2018, the first ever neutrino registration from an extragalactic source was announced. Moreover, this event was only the third unambiguous identification of neutrinos from an astronomical source after the Sun and supernova 1987A. The source of the event, caught by the IceCube Antarctic installation on September 22, 2017, was blazar TXS 0506 + 056 – an active galaxy, the emission from the center of which is directed close to the line of sight.
Blazars are the active nuclei of galaxies, a subtype of quasars in which jets are directed at a slight angle to the line of sight, due to which the radiation of the jet dominates the spectrum of the source, its brightness increases for the observer, but can undergo sharp fluctuations. The blazar energy release mechanism is associated with the fall of matter onto a supermassive black hole in the center of the parent galaxy, some of which are thrown out in the form of narrow jets with a near-light speed.
TXS 0506 + 056 is located at a redshift of 0.34, and the light from it went to Earth 3.8 billion years. Although this blazar is a bright source, it is inferior in brilliance to many other active galaxies. Also, the high-energy radiation in the gamma range of a number of other galaxies is much more intense than that of TXS 0506 + 056. In this regard, the observation of a high-energy particle from this particular source was unexpected and required a separate explanation.
The work of astrophysicists from Germany, South Africa, Russia, the Czech Republic and Georgia under the leadership of Silke Britzen of the Radio Planning Institute of the Max Planck Society describes a new analysis of the observation of the TXS 0506 + 056 nucleus by radio interferometry, which made it possible to suggest a possible neutrino production mechanism. It turned out that the relativistic jet near the nucleus at the parsec scale has a complex structure and an anomalously high curvature, which should be associated with interacting flows of matter.
It is generally believed that the plasma in the jet moves relatively without disturbance, but in TXS 0506 + 056 this was not the case. In this case, the apparent velocity of the substance at the end of the jet is greater than at the beginning. The authors suggest that this can occur either during the formation of a strongly curved jet due to the collision of the jet substance with the mothers ejected earlier from the vicinity of the black hole, or in the case of the intersection of two jets – this situation may occur in the case of a double supermassive black hole in the center of the object.
Astronomers also recorded a precession of the inside of the jet, that is, a change in its direction, with a period of about 10 years. Despite the fact that jet precession can occur in double black hole systems, in this case, this scenario explains the observations worse, since the distance between active nuclei is too large to create a precession with the desired period. At the same time, a suitable influence can be caused by the Lense-Thirring effect, that is, the entrainment of space-time near rapidly rotating massive bodies, for example, a black hole.
Regardless of the scenario, extremely high-energy neutrinos should have been produced when matter collided in relativistic jets if they were successfully oriented relative to the observer on Earth. The authors believe that the measured parameters of the jets in TXS 0506 + 056 create suitable conditions for the generation of neutrinos. Scientists also separately note that the hypothesis of a double black hole in this source is interesting in itself, since there have not yet been unambiguous registrations of such objects with such a small distance between components.