Scientists from NASA found a high concentration of carbonate deposits in the western region of the Jezero martian crater, which suggests that there could have been a lake in this area before. Certain types of sediments located along the edges of the crater may contain evidence of the vital activity of ancient microorganisms and the existence of a stable ecosystem. Earlier, the Jezero crater was chosen for the landing of the Mars 2020 rover, as it is located in one of the areas with a high carbonate content: scientists knew about their presence in the crater, but only now they have conducted a detailed geological study of their composition.
In 2008, in several places on the Martian terrain, astronomers using remote sensing discovered carbonates – minerals that appear on Earth as a result of the interaction of CO 2, water and rock. Carbonates, which precipitate in the aquatic environment, well preserve the remnants of the vital functions of microorganisms, and on Mars, they could be formed only if there is a rich carbon dioxide of the atmosphere and a relatively humid climate.
Such conditions, according to the predictions of scientists, could exist on Mars 3.8-4 billion years ago, in particular, in the crater of Jezero. Previous studies have shown that in some places along its edges there are bays, deltas and channels with bends and deposits of soil that are characteristic of the processes of influx and outflow of water, so scientists believe that there used to be a lake in this place.
Carbon-containing regions attract scientists with the opportunity to find on Mars evidence of the existence of ancient life – stromatolites. These are rocky structures that are formed along the coasts of microorganisms on Earth. They are formed together with deposits of carbonates, which served as material for mollusc shells and for corals.
A team of scientists led by Briony HN Horgan from Purdue University conducted a detailed spectral analysis of the Jezero Crater. They obtained the most important data using a CRISM spectrometer installed on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter satellite. Of particular interest was the western delta: it underwent less erosion than other similar formations.
Scientists have received 10 unique pictures of the delta and adjacent areas. By the nature of the spectrum, they determined the chemical composition of mineral deposits, and also calculated the quantitative ratio of carbonates and their related components in sediments.
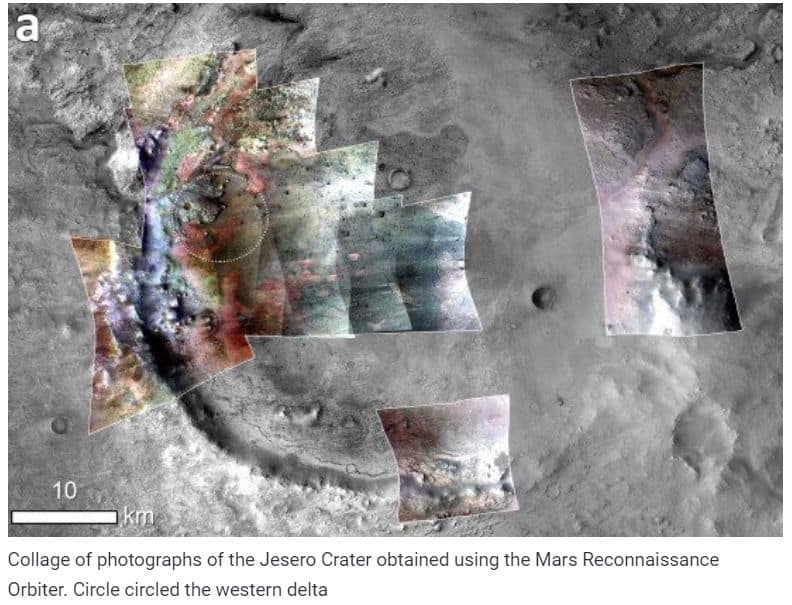

As a result of the analysis, the highest concentration of carbonates was found between the western delta and the edge of the crater. The mineral composition of the deposits turned out to be more diverse than scientists assumed. In particular, scientists separated “coastal carbonates”, since their deposits extend only along a narrow strip of the crater, are much more distinct in the spectrum and differ from other carbonates in this region in mineralogical composition. The composition of “coastal carbonates” turned out to be similar to the composition of stromatolites and similar lacustrine deposits on Earth. In such deposits, the remains of microorganisms in the form of biofuels, isotopes, individual organic particles and biominerals are preserved.
The Mars 2020 rover, which is scheduled to launch in August 2020, will look for signs of microorganisms. The mission’s program is based on data from the Curiosity rover. Mars 2020 will seek evidence of the remnants of ancient life by collecting soil samples and will return to Earth for analysis during future missions.
Researchers do not claim that mineral deposits formed during the existence of the lake: they could have appeared even before that. However, “coastal carbonates” are of great interest for the future Martian mission. Since the Jezero crater was originally chosen as the place for landing and operation of the rover, scientists will be able to send it to the desired areas of the western delta to get soil samples from there.
