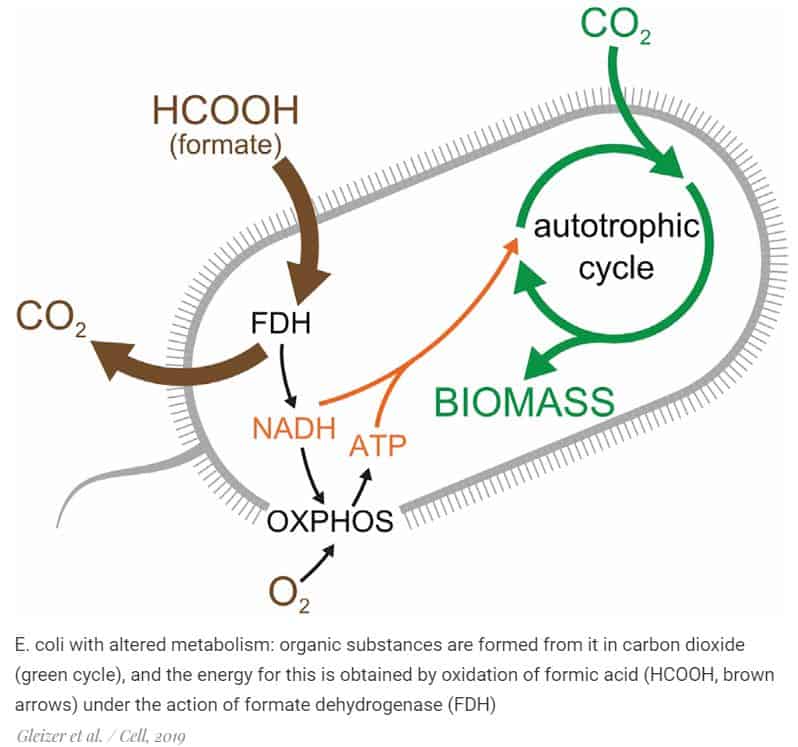
A team of scientists from Israel have received a strain of E. coli (Escherichia coli) capable of autotrophic nutrition, according to study. Bacteria obtained in the laboratory through genetic engineering and breeding are able to create organic matter from carbon dioxide during the Calvin cycle reactions. It is expected that such Escherichia coli will promote the biosynthesis of substances necessary for humans on an industrial scale without waste in the form of carbon dioxide.
Biotechnology has long been able to incorporate the genes of other organisms into the DNA of bacteria and make these genes express, and as a result of their expression, the necessary substances are formed. So on an industrial scale receive a number of hormones (insulin, growth hormone somatotropin), amino acids and other substances. Most of the bacteria that are used for this purpose are heterotrophs. This means that they need other organic substances to produce organic substances. This is different from the autotrophs, which inorganic raw materials – carbon dioxide (CO2) are suitable for the creation of organics. Autotrophs absorb it from the air and include in the composition of larger molecules, a process called carbon fixation.
Given that the CO 2 content in the planet’s atmosphere is growing, and the climate is changing along with it, it would be nice to switch bioproduction to a non-waste mode, to “teach” bacteria to synthesize organic substances from carbon dioxide, which they themselves (or someone else ) and produced while breathing. Various groups of scientists have already attempted to do this, but the bacteria obtained in the course of their experiments nevertheless required some organic substances to fix carbon. In the best case, such organisms formed only one-third of the biomass from carbon dioxide.
Researchers at the Weizmann Institute of Science, led by Ron Milo, have developed Escherichia coli, which can use only carbon dioxide to produce organics without adding any organic matter. To do this, they added the genes of enzymes necessary for the reactions of the Calvin cycle to Escherichia coli DNA (during which CO 2 turns into organic substances), inactivated some of the enzymes necessary for normal metabolism to heterotrophs, and placed the resulting bacteria in bioreactors, where the atmosphere contains 10% carbon dioxide, and not 0.4%, as terrestrial.
Several generations of bacteria were kept in bioreactors, adding some xylose sugar to the medium so that heterotroph microorganisms could survive. Xylose is not the most convenient source of carbon; therefore, bacteria capable of producing carbon from carbon dioxide gained an advantage in such an environment. They were first isolated from bioreactors 203 days after the start of the experiment, and by 340 days all bacteria were able to use CO 2 as a material for building organic substances.
The energy for the fixation of carbon was the oxidation reaction of formic acid. Although this substance is organic, its E. coli atoms were not included in the composition of organic molecules, which means that formic acid, by definition, did not support heterotrophic metabolism.
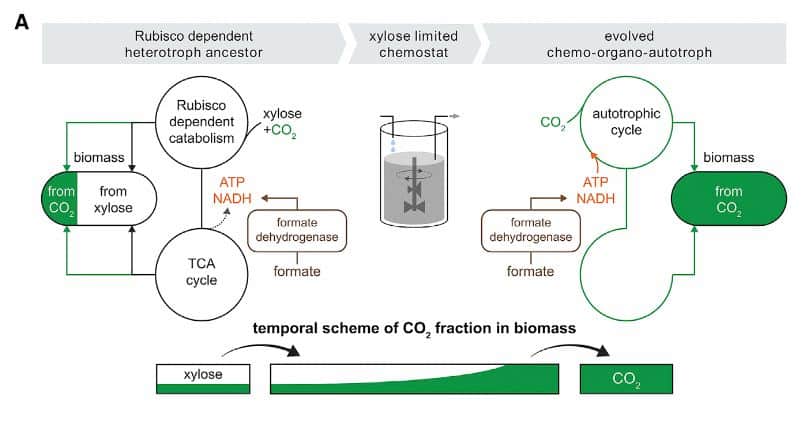
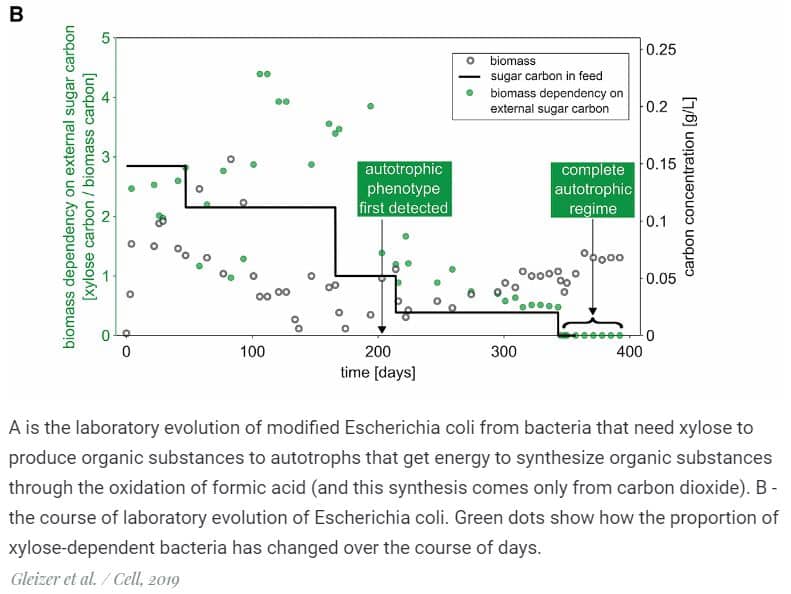
The experiment showed that known bacteria can be “tuned” in the foreseeable time so that they produce organic matter only from carbon dioxide. True, while the resulting Escherichia coli produce more CO 2 during the oxidation of formic acid, than they absorb it for the Calvin cycle. In addition, there is no absolute certainty that autotrophic Escherichia coli can also be easily grown on an industrial scale, new studies are needed to study this issue.