A Canadian researcher says that since the 1980s, an ozone hole seven times bigger than the one in Antarctica has been sitting over tropical regions.
Scientist Qing-Bin Lu from the University of Waterloo in Ontario, Canada, reports in AIP Advances that there is a large, all-season ozone hole in the lower stratosphere over the tropics that is similar in depth to the well-known springtime Antarctic hole but has an area that is roughly seven times larger. An ozone hole is defined as an area of ozone loss larger than 25% compared with the undisturbed atmosphere.
“The tropics constitute half the planet’s surface area and are home to about half the world’s population,” says Lu. “The existence of the tropical ozone hole may cause a great global concern.

“The depletion of the ozone layer can lead to increased ground-level UV radiation, which can increase risk of skin cancer and cataracts in humans, as well as weaken human immune systems, decrease agricultural productivity, and negatively affect sensitive aquatic organisms and ecosystems.”
Since it was not predicted by traditional photochemical models, Lu’s observation of the ozone hole came as a surprise to his peers in the scientific world. His observations are consistent with the cosmic-ray-driven electron reaction (CRE) model and strongly suggest that the same physical process is at work for both Antarctic and tropical ozone holes.
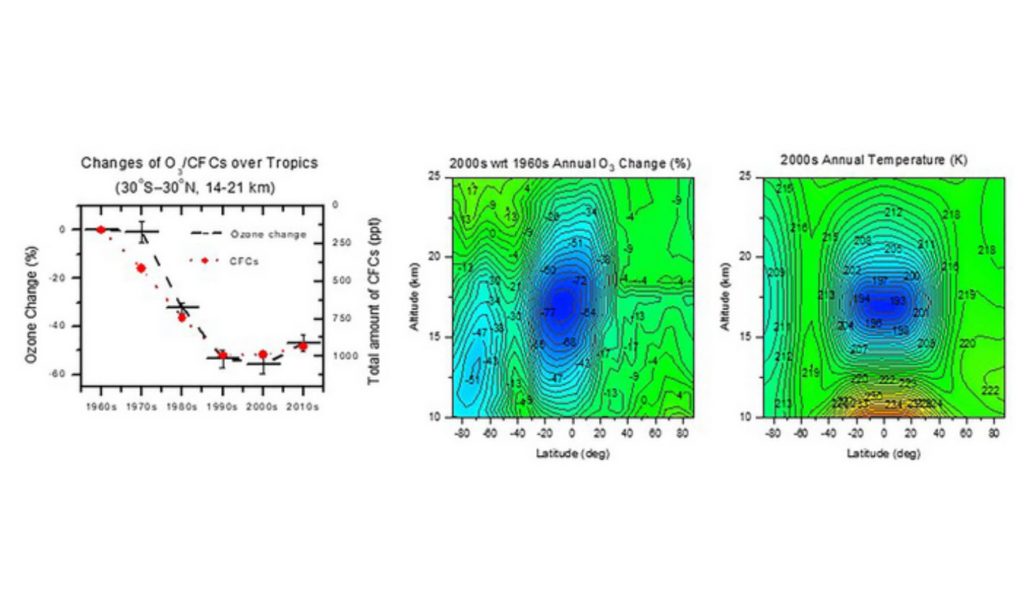
Similar to the polar ozone hole, the core of the tropical ozone hole contains around 80 percent of the usual ozone value. According to preliminary reports, ozone depletion levels over equatorial regions are already putting a lot of people in risk, and the UV radiation that results from this radiation is far worse than anticipated.
In the middle of the 1970s, atmospheric research revealed that industrial chemicals, particularly chlorofluorocarbons(CFCs), may be contributing to the ozone layer’s depletion, which absorbs the majority of the sun’s ultraviolet energy. The Antarctic ozone hole was first discovered in 1985, confirming that CFCs are to blame for ozone loss. However, research suggests that ozone depletion continued even after such substances were banned.
According to Lu, the emergence of three “temperature holes” in the global stratosphere mirrors how the tropical and polar ozone holes significantly contribute to cooling and controlling stratospheric temperatures. He claimed that understanding global climate change may depend on this discovery.
Lu’s discovery expands on earlier research into the CRE-initiated ozone-depleting mechanism, which he and his coworkers first put forth roughly 20 years ago.
The current discovery necessitates further thorough research into how ozone depletion, UV radiation shift, elevated cancer risks, and other detrimental effects on human health and tropical ecosystems are affecting these areas, according to Lu.
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: “New” Ozone Hole Is Actually Much Larger Than Antarctic And Threatens 50% Of Earth’s Population
