American engineers have created a system for remote control of an experimental bipedal robot. Its difference from most such systems is that the operator not only controls the movement of the robot but also receives feedback – for example, when the robot is pushed. In addition, the developers used the system to the proportional transmission of movements, taking into account the difference in size, mass and construction between man and robot.
In recent years, the field of walking robots has seen a sharp jump in development. Some developments, such as Boston Dynamics’ Atlas robot, already have impressive capabilities. However, they are not enough for full use. For example, one of the most promising applications of bipedal robots is the elimination of the consequences of natural and man-made disasters. In order for the robot to fully replace lifeguards, it must not only walk through the ruins, keeping balance, but also open the doors, turn the cranes, move Large designs and perform other simple actions for humans, but it is still difficult for machines.
The creation of universal robots has an alternative in the form of telecontrol. This allows for partial use instead of sophisticated human control algorithms and sensors. However, many existing tele-controlled robots have drawbacks. The main one is that many of these developments do not have feedback. In addition, even if it is, the synchronization of movements between the operator and the robot usually does not take into account the difference in proportions, speed of movement and other important parameters.
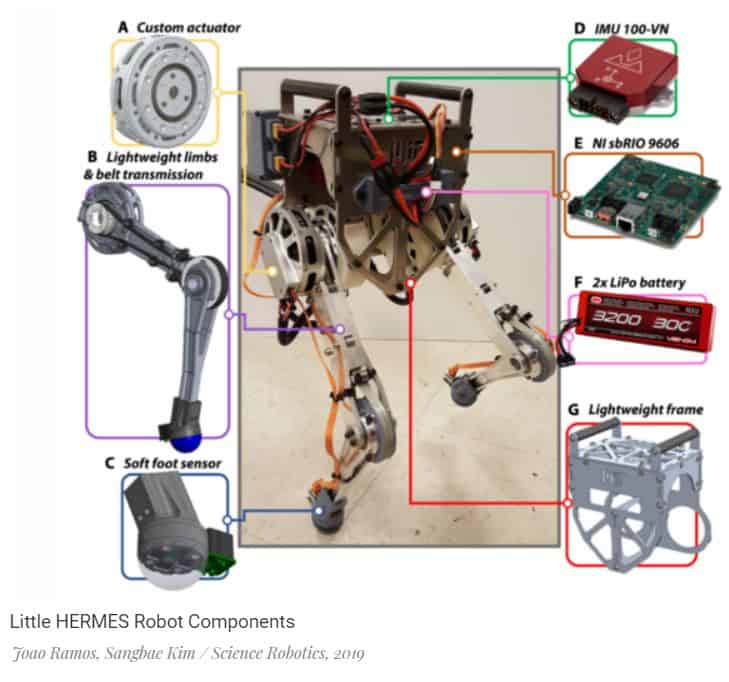
Joao Ramos of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Sangbae Kim of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology have created a two-legged Little HERMES robot, which is named after analogy and larger HERMES robot. It is a two-legged structure with two-section legs. Between themselves, as well as with the general centre of the legs are connected by powerful actuators. In addition, four piezoelectric pressure sensors are installed at the base of each leg. Since engineers solved a particular problem within the framework of this work, rather than creating a full-fledged universal robot, it is fastened with a barbell that holds it and does not allow to fall forward Or backwards.
The robot is controlled by commands from the stand on which the operator is located. Like the robot, it is mechanically connected to the stand using two-section rods from below (one for each leg) and two on top, attached through the vest. In addition, the floor on which the operator stands is mounted on pressure sensors, which allows calculating the force with which the legs press on the floor.
Movements between the operator and the robot are not synchronized directly. Instead, the developers created two models describing the operator and the robot. Engineers simplified the task to the reverse pendulum, consisting of the centre of the masse from above and the hard rod. This pattern of motion data transmission allows to correctly transmit movements between the operator and the robot, taking into account the difference in size.
The authors showed in the video examples that the robot is able to repeat human movements when stepping and bouncing up. In addition, the video can be seen that if the robot is pushed, it transmits movement to the person, and compensates for the external impact, thereby saving himself and the robot from falling. Finally, the engineers checked the pattern with stabilization not in the transverse, but in the longitudinal plane, in which the robot moves forward when the person walks on the spot.
Remote-controlled robots were previously created by other engineers. For example, in 2017, such robot was introduced by Toyota. And European engineers from 2018 develop the project of tele-controlled robot centaur. At the end of the year, they taught him to read the position of the human body and repeat it. Thus, you can not only move the robot but also, for example, lift objects.
