A team of physicists from Nanjing University have described and demonstrated the possibility of obtaining four-dimensional images using an array of microlenses from liquid crystals. The created device simultaneously allows you to restore the three spatial coordinates of objects in the field of view, as well as the degree of polarization of the light reflected from them. The proposed scheme may become the basis for a new type of cheap sensors.
Conventional cameras, like human eyes, get a two-dimensional image. The sense of three-dimensionality is created by additional means: depth of field, saccades, binocularity, change of perspective, image processing and so on. However, it is also possible to obtain truly three-dimensional images that contain comprehensive information about the position of all captured objects in all three spatial axes. This is implemented in many microscopy techniques, such as confocal microscopy, optical coherent tomography or atomic-force microscopy.
These techniques use complex and expensive equipment, have internal limitations, and often require multiple frames to restorer 3D imaging and sophisticated computer processing techniques, which slows down the results and reduces the potential for application.
However, light has additional characteristics, primarily polarization, which are also important in many technical and natural circumstances. Special cameras have also been developed to record polarization, but they are also usually voluminous and expensive. The exceptions are systems based on passive polarimeters, but they are only now beginning to appear.
A combination of a three-dimensional image and at least one polarization parameter would produce four-dimensional images containing a wealth of information useful in the context of materials exploration, navigation and the interaction of living things. However, so far a convenient device with such capabilities has not been created.
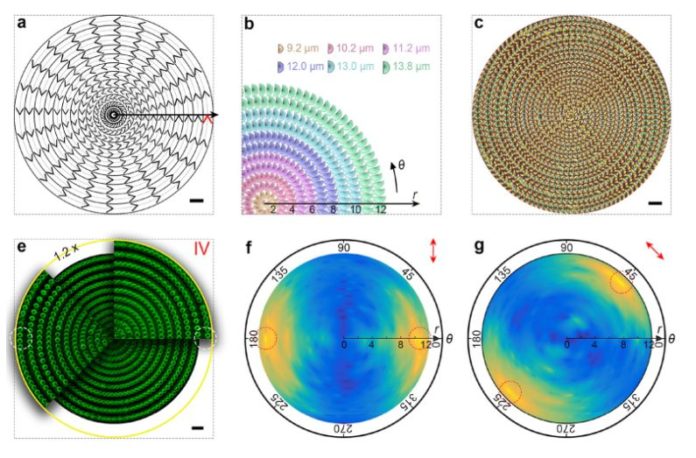
Recently, a team of Chinese scientists led by Yan-qing Lu from Nanjing University have proposed a new approach to the creation of a similar camera, based on an array of small lenses in which in liquid crystals act as a refractive environment. The idea is to create a superstructure of small lenses: from the centre to the edge increases the size of the lenses, which sets different focal distances, and in a circle changes orientation liquid crystals, which determines transparency for this polarization.
As a result, it becomes possible to obtain a four-dimensional image in a single frame: each microlens builds its own two-dimensional image, and the position of the sharpest among all obtained allows you to determine the distance to the object and the degree of polarization. Physicists have confirmed the feasibility of the idea by creating the appropriate lens. At the moment, the device has limited capabilities, but the authors note that their goal was only an experimental justification, while there remains the potential for optimization.