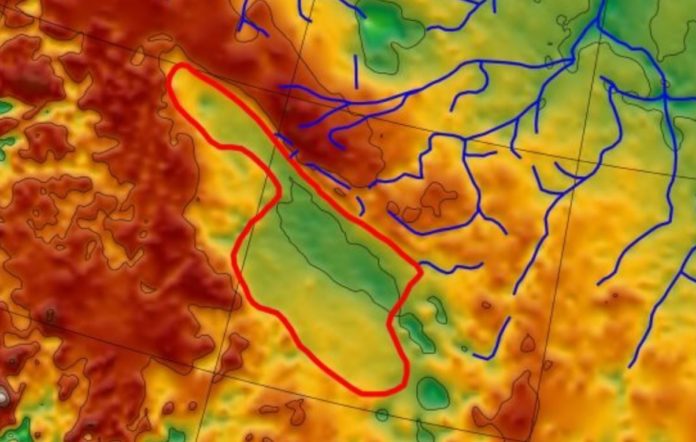
Scientists have discovered an enclosed palaeo-lake under an ice sheet in northwestern Greenland. Geomorphological analysis and hydrological modeling showed that the lake covered an area of up to 7100 square kilometers.
Under the Greenland ice sheet, scientists from Columbia University (USA) have discovered deposits of a huge basin of an ancient lake. Apparently, this palaeolake maybe hundreds of thousands or millions of years old and contain unique fossils and chemical traces of past climate and life. The research is published in the journal Earth and Planetary Science Letters.
Previously, geologists have already found subglacial lakes – containing water in liquid form, “sandwich” between rock and ice – both in Greenland and Antarctica. However, the recently discovered palaeolake was most likely formed when there was no ice in the area where it was located.
Scientists have mapped the outlines of the lake’s bottom with its lowlands and hills, and also studied data from airborne geophysical instruments that can read signals penetrating through the ice and provide images of the geological structures below. Most of the information was obtained from aircraft flying at low altitude above the ice sheet as part of the NASA IceBridge mission.
According to the researchers, the lake, located at the site of the discovered traces of the basin, reached an area of about 7100 square kilometers, and its depth was estimated at 50-250 meters. Geophysical images have revealed a network of at least 18 stream channels carved into the adjacent bedrock on the sloping escarpment to the north that most likely fed the lake. At the same time, at least one stream exited to the south.
It is impossible to determine the exact age of the palaeolake: it is likely that ice has periodically advanced and retreated over most of Greenland over the past 10 million years, and possibly 30 million years. Gravity measurements have shown that the rocks in the basin are less dense than those around it: this suggests that the bottom consists of sediments washed away from the sides. Moreover, their thickness reaches 1.2 kilometers.
The rocks washed from the edges of the ice sheet turned out to contain remnants of pollen and other materials: Greenland probably experienced periods of warmth over the past million years, which allowed plants and even forests to survive. However, the evidence is not conclusive as such disparate rocks are difficult to date.
As the authors of the work explain, the basin they discovered may prove to be “an important place for future under-ice drilling and study of sediments, which can provide valuable information about the glacial, climatological and ecological history” of the region. However, due to the fact that the top of the ancient rocks is 1.8 kilometers below the current ice surface, drilling will be difficult, although not impossible.