Artificial intelligence-designed Xenobots demonstrate an altogether new mechanism of biological self-replication, which holds great promise for regenerative medicine.
Researchers at the University of Vermont, Tufts University, and Harvard University uncovered a novel mode of biological reproduction—and developed self-replicating living robots.
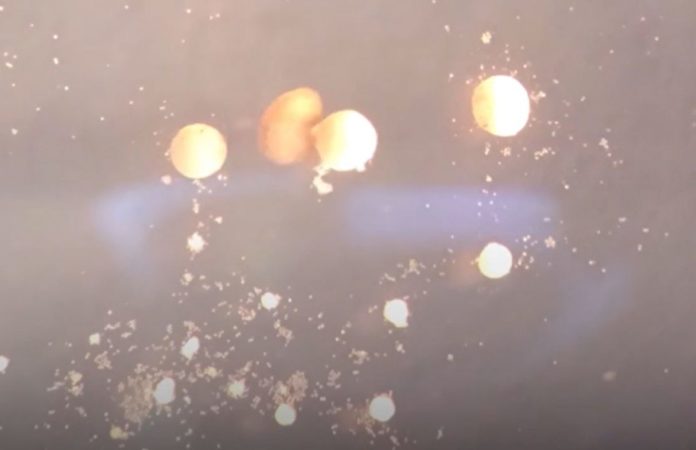
These computer-designed animals, composed of frog cells, collect single cells within a Pac-Man-shaped “mouth” and release Xenobot “babies” that look and move like themselves. Then the offspring repeat the process.
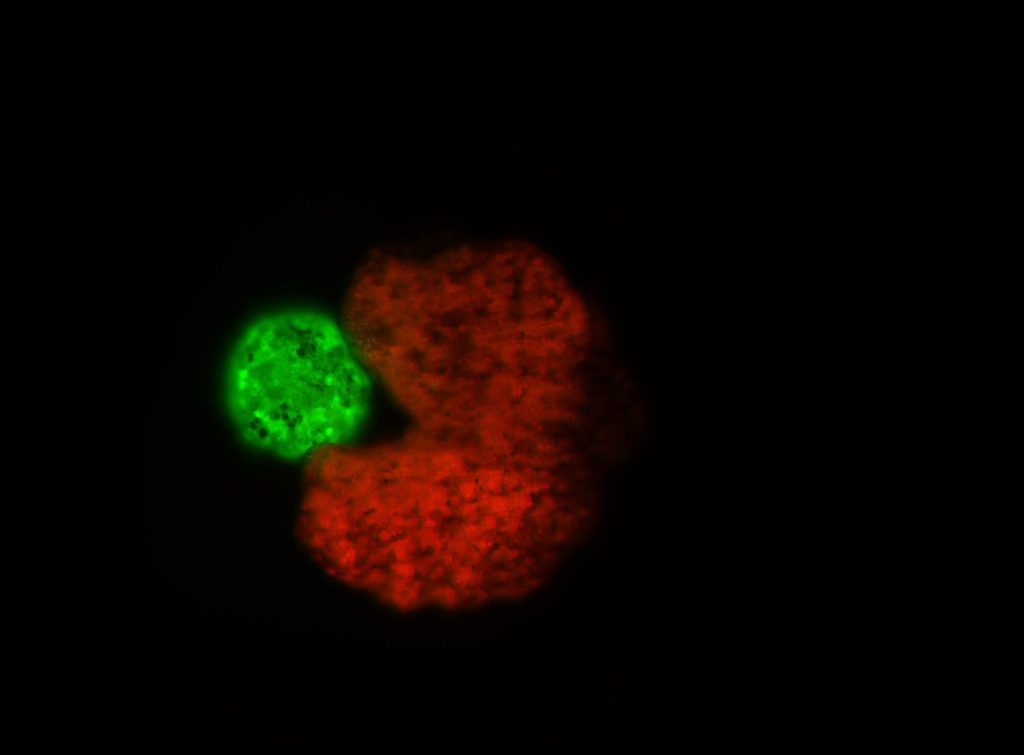
Josh Bongard, University of Vermont; Michael Levin, Tufts University and the Wyss Institute at Harvard University; Douglas Blackiston, Tufts University; and Sam Kriegman, Tufts University and the Wyss Institute at Harvard University invented and collaborated on Xenobots.

Source: 10.1073/pnas.2112672118
Image Credit: Tufts and ICDO
You were reading: Xenobots 3.0: scientists create world’s first living robots that can reproduce – video
