Freeze-drying is a process that removes moisture or water from a substance or product. Astronaut food is one example of a freeze-dried product or emergency rations or maybe some future COVID-19 vaccines.
What is the freeze-drying method?
To begin, you freeze the item you’re attempting to dehydrate, converting any remaining water to ice. The ice is then removed via a process known as sublimation, in which ice converts straight to vapor under low pressure.
How the freeze-drying process can be used for COVID-19 vaccines?
According to a new study, scientists successfully freeze-dried a liposome-based liquid vaccination formula that might be used in COVID-19 vaccines.
A vaccination based on freeze-dried liposomes is still years away. However, if produced effectively, dehydrated doses may be shipped and stored at room temperature, addressing logistical issues connected with some of the most widely used vaccinations now available.

“At the time we started this project, the first COVID-19 vaccines were just getting rolled out, and there was a lot of news about how they needed ultra-cold storage, and how that was a huge logistical challenge. Especially in low- and middle-income countries, it may not always be feasible to have that type of refrigeration infrastructure. So we started to look at whether we could make a thermostable COVID-19 vaccine using a liposome-based vaccine platform that we worked on previously,” said Jonathan Lovell, senior author of the study.
The current research focuses on a liquid injection made up of water, specialized liposomes containing a synthetically generated version of the COVID-19 virus’s spike protein, and a little amount of sugar to help protect the formula throughout the freeze-drying process.
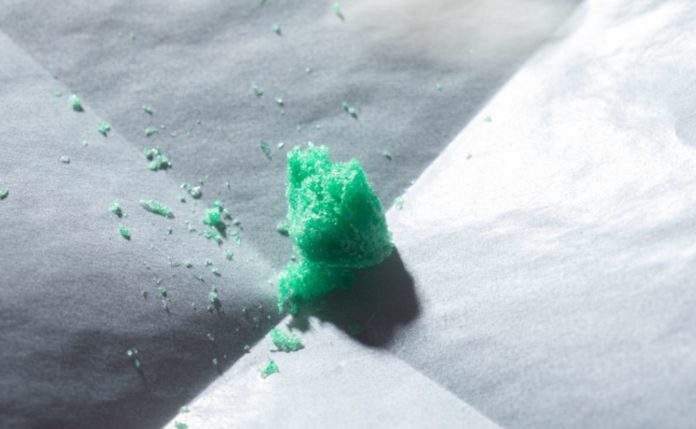
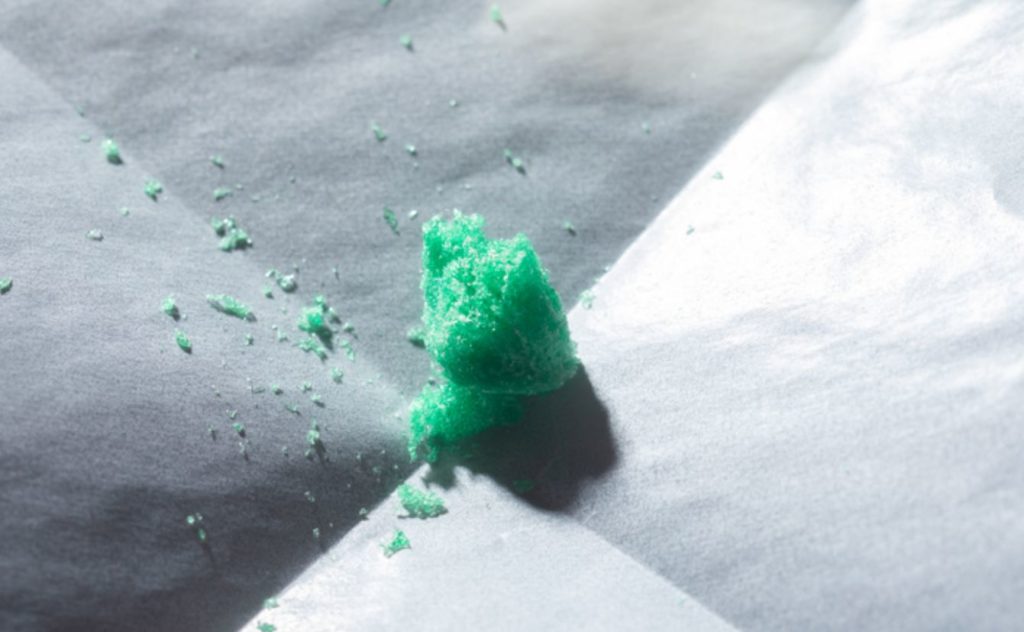
The freeze-dried product has a mint green tint that resembles cotton candy.
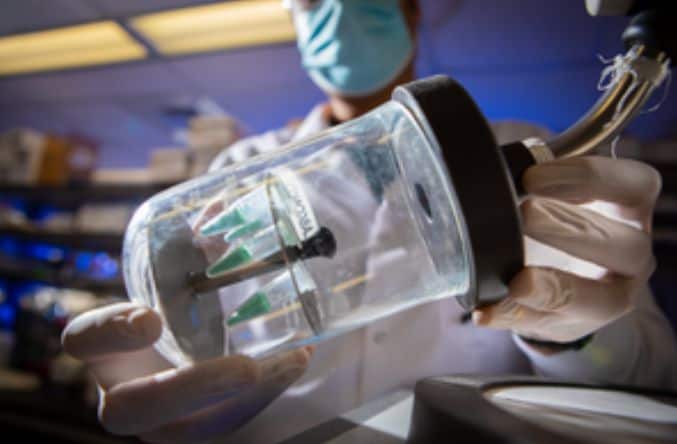
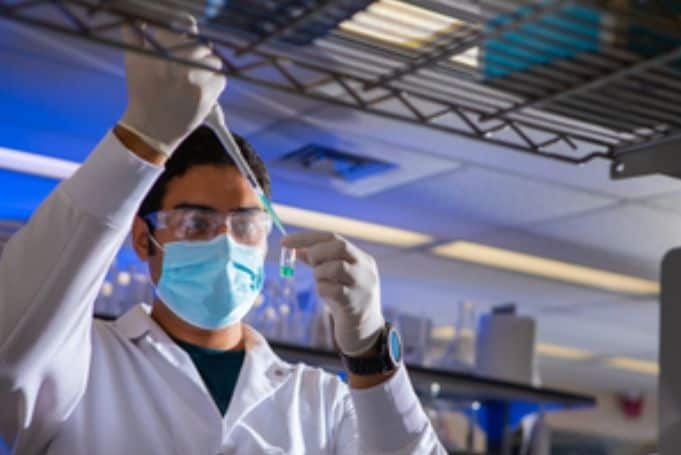
“Upon dehydration, the formula was stable at elevated temperatures, and we showed that it can withstand room temperatures and even higher temperatures for at least a week,” said Moustafa Mabrouk, first author of the study.
“After that, we reconstituted the formula by adding water. When we tested this in mice, it induced effective antibody responses and offered protection against the COVID-19 virus.”
The customized liposomes studied in Science Advances are being investigated for application in vaccines against a variety of diseases. The liposomes were created in Lovell’s UB lab and were licensed by the university to POP Biotechnologies, a startup that Lovell co-founded.

In South Korea, a COVID-19 vaccine candidate based on POP Biotechnologies’ liposome-based vaccine delivery method is undergoing human testing. POP Biotechnologies and EuBiologics, a South Korean biotech business, are working on a vaccine candidate dubbed EuCorVac-19. The components of EuCorVac-19 differ slightly from the vaccine composition evaluated in the Science Advances publication.
“We have not tested freeze-drying on the EuCorVac-19 vaccine,” said Lovell.
“However, I think the data in this new study suggest that, in theory, the EuCorVac-19 formula may be amenable to this type of treatment to make it very thermostable, which would benefit any global deployment.”
Source: 10.1126/sciadv.abj1476
Image Credit: DOUGLAS LEVERE / UNIVERSITY AT BUFFALO
You were reading: Freeze-drying: it can help store mRNA vaccines at room temperature, study shows
