This groundbreaking research has answered a long-standing conundrum in immunogenetics.
MHC class I or MHC class II? For decades, scientists have questioned which of these two classes evolved first.
In a new PNAS paper, Keiichiro Hashimoto and his team at Fujita Health University, Japan, solve this question alongside European collaborators.
They found MHC-W, an ancient MHC molecule category that explains how class I molecules developed from class II-like origins.
“In demonstrating that MHC class II evolved prior to MHC class I, which evolved from MHC class II, this landmark study has resolved an important and outstanding puzzle in immunogenetics,” says PNAS guest editor Peter Parham.
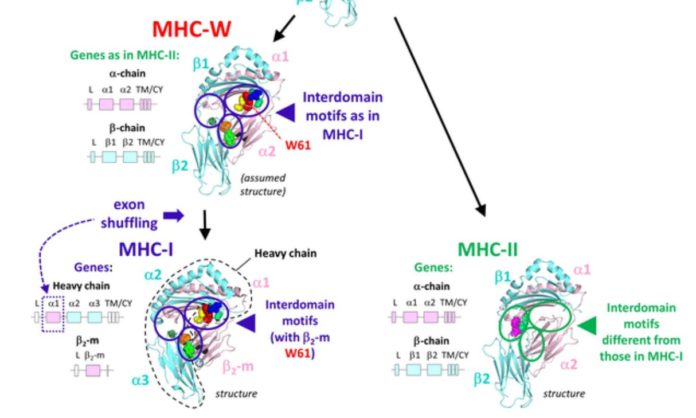
The molecules of MHC class I and class II are linked. Both kinds have four extracellular domains, with the two membrane-distal domains forming a groove for binding T lymphocyte-presented peptides. Class II molecules, on the other hand, are made up of two transmembrane chains of comparable size, one with the extracellular II-α1 and II-α2 domains and the other with the extracellular II-β1 and II-β2 domains.
Class I molecules, on the other hand, are made up of a large transmembrane heavy chain with three of the four extracellular domains (I-α1, I-α2, and I-α3) and a single domain beta-2 microglobulin (β2-m) molecule (Fig. 1).
The following class I and class II domains correspond to one another in the structures: II-α1 with I-α1, II-α2 with β2-m, II-β1 with I-α2, and II-β2 with I-3. Jim Kaufman and co-workers postulated in 1984, based on domain similarity levels and parsimony considerations, that MHC molecules started out as a homodimer, followed by gene duplication and differentiation, leading to a heterodimer that served as the origin of both extant class I and class II (Fig. 1).
However, their conclusion was disputed, and the question of which came first remained unanswered until now. Importantly, no primitive MHC with both class I and class II traits has been discovered, which could shed information on evolution’s trajectory.
The Hashimoto group may acquire more solid phylogenetic tree analysis support for the Kaufman model by having access to many more MHC sequences from many more species than Jim Kaufman had in 1984.
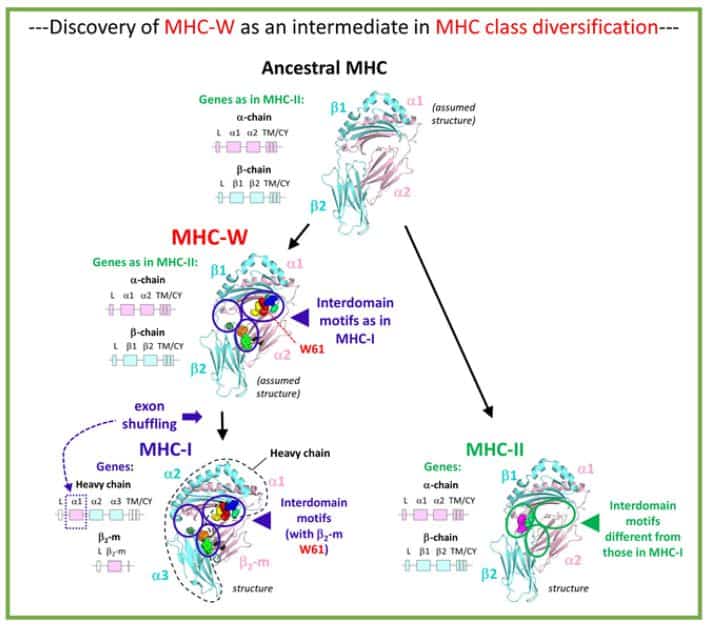
Most crucially, the Hashimoto group found a new class of MHC molecules known as “MHC-W” in primitive jawed vertebrates such as sharks, ray-finned fishes, lobe-finned fishes, and salamanders, which had sequences identical to class I but smaller alpha and beta transmembrane chains than class II (Fig. 1).
This concludes that MHC molecules with similar-sized alpha and beta transmembrane chains originated first in evolution, which supports the Kaufman hypothesis. MHC-I and MHC-W are distinguished from MHC-II by interdomain binding motif residues at the precise sequence level. MHC-W molecules contain residues of the unique key motifs discovered in MHC class I complexes for binding of β2-m, including a crucial tryptophan (W in single letter coding) in the β2-m/Wα2 domain, which gave the MHC-W moniker (Fig. 1).
This shows that the mechanism for binding β2-m evolved before exon shuffling events resulted in an MHC-W ancestor with a heavy chain plus β2-m class I scenario (Fig. 1).
“The research described in Okamura et al. to be published in PNAS is a tour-de-force, with a completely novel and unexpected MHC gene family strongly supported by different kinds of data collected over many years from a range of non-mammalian vertebrate species,” says Jim Kaufman, a former professor at the University of Cambridge who is now a professor at the University of Edinburgh, adding, “the scenario proposed by the lab of Hashimoto is the first advance in many decades for understanding the early evolution of MHC genes.”
Apart from demonstrating that the II-type chain-length organization emerged first in MHC evolution, MHC-W may also aid in the future elucidation of another long-standing riddle in MHC science, namely the mechanism of β2-m function.
You were reading: Landmark study solves an important and outstanding MHC class divergence puzzle