Studying the Earth’s metallic core, researchers have found that helium that was produced shortly after the Big Bang has been leaking out.
The great bulk of this gas in the universe, known as helium-3, is primordial, having formed just after the Big Bang 13.8 billion years ago. Some of this helium-3 would have mixed with other gases and dust particles in the solar nebula, the enormous, swirling, and collapsing cloud considered to have spawned the solar system.
According to the researchers, the discovery that Earth’s core likely includes a massive pool of helium-3 adds to the evidence that Earth formed amid a thriving solar nebula, rather than on its periphery or during its declining phase.
Helium-3 is an isotope, or variation, of helium with one neutron in its nucleus instead of the typical two. It’s a rare gas, accounting for only 0.0001% of all helium on the planet. It is produced by a variety of mechanisms, including the radioactive decay of tritium, a rare radioactive hydrogen isotope. However, because helium is one of the first elements in the cosmos, most helium-3 is thought to have originated with the Big Bang.

Scientists already knew that roughly 4.4 pounds (2 kilograms) of helium-3 escapes from Earth’s interior each year, primarily in the mid-ocean ridge system where tectonic plates collide, according to the study.
However, scientists were unsure how much helium-3 came from the core versus the mantle, or how much was in Earth’s reservoirs.
To find out, the researchers modeled helium abundance during two key periods in Earth’s history: early formation, when the planet was still acquiring helium, and after the formation of the moon, when our planet lost a significant amount of this gas. Scientists believe the moon formed around 4 billion years ago when a massive asteroid the size of Mars crashed with Earth.
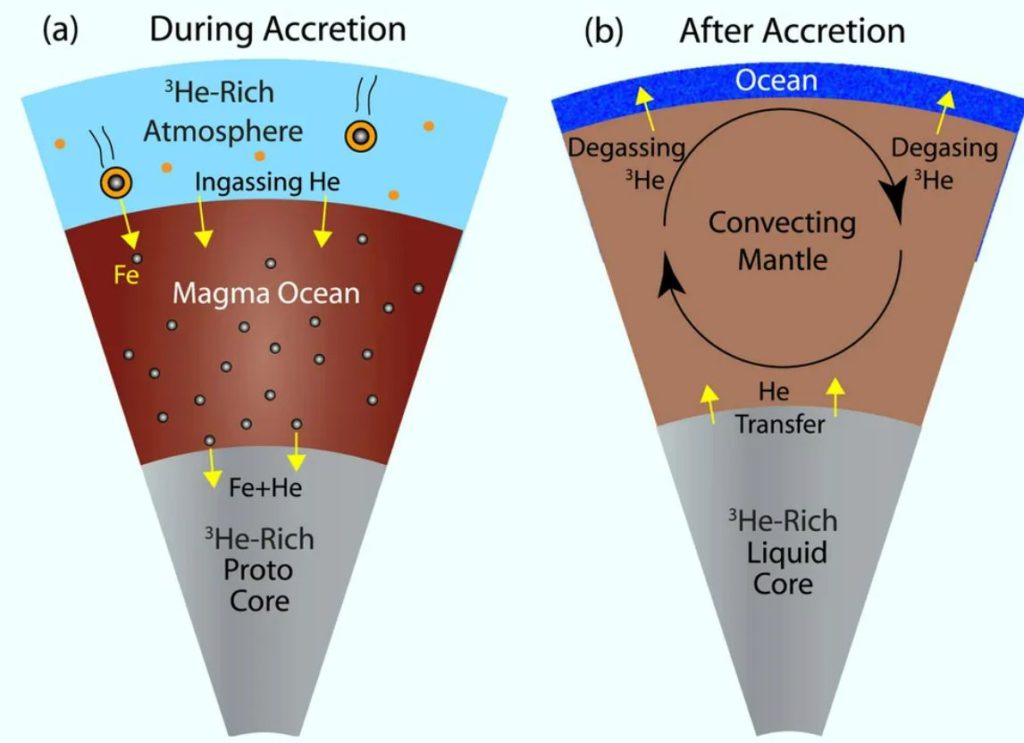
This occurrence would have burned the Earth’s crust, allowing much of the helium within our planet to escape.
The Earth, on the other hand, did not lose all of its helium-3 at that time. It still contains some of the rare gas that seeps out of Earth’s interior. The core would be an ideal location for such a reservoir because it is “less vulnerable to large impacts compaared to other parts of the Earth system,” according to the researchers, and it is not affected by tectonic plate cycling, which releases helium gas.
The researchers used models of helium isotope dynamics to combine modern helium-3 leak rates. According to these estimations, Earth’s core contains between 22 billion pounds (10 teragrams) and 2 trillion pounds (1 pentagram) of helium-3, a tremendous amount indicating that Earth formed in a solar nebula with significant helium-3 concentrations.
The metallic core is implicated in their models of gas exchange during Earth’s origin and evolution as a leaky reservoir that provides helium-3 to the rest of the Earth, the researchers said in the report.
The results aren’t infallible, though, because they’re based on modeling. The researchers had to make several assumptions, including that Earth absorbed helium-3 when it originated in the solar nebula, that helium penetrated core-forming metals, and that some helium departed the core for the mantle. These assumptions, combined with other unknowns such as how long the solar nebula lasted in comparison to the rate at which Earth formed, suggest that there may be less helium-3 in the core than the scientists estimated.
However, the researchers aim to find more evidence to back up their findings. Finding additional nebula-created gases, such as hydrogen, escaping from Earth from identical areas and at similar rates as helium-3, for example, might be a “smoking gun” indicating that the core is the source, according to the authors.
Image Credit: shutterstock
