Scientists at Scripps Research have created a medication that stops SARS-CoV-2 from attaching to ACE2 receptors and infecting human cells. When the drug-coated virus approaches the receptor, it attaches a “nitro group” to ACE2 in the same way that nitroglycerin does.
A breakthrough drug developed by researchers at Scripps Research can turn the COVID-19 infection into its own harbinger of doom.
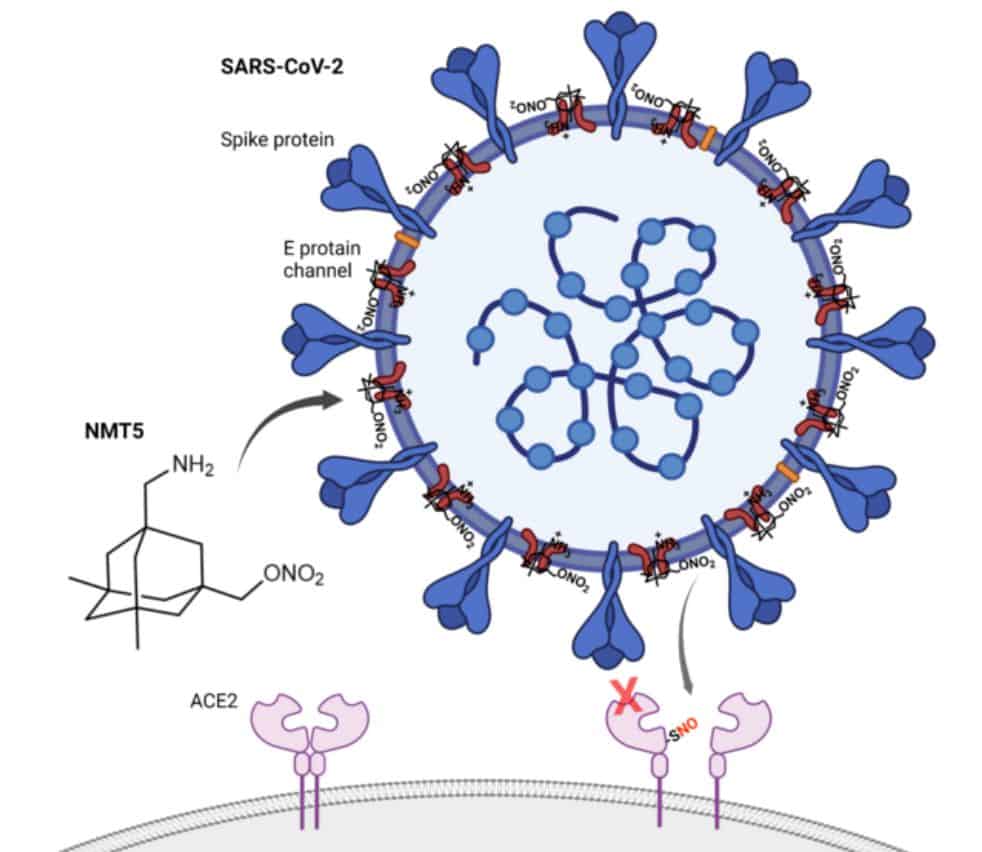
As detailed in Nature Chemical Biology, the drug NMT5 coats SARS-CoV-2 with chemicals that can temporarily change the human ACE2 receptor, which is what the virus normally uses to get into cells. This means that when the virus is close, it can’t get into human cells through the ACE2 receptor. But when the virus isn’t around, ACE2 can work as usual.

The Step Family Endowed Chair and Scripps Research Professor Stuart Lipton, MD, PhD, the senior author of the study, explains that the drug’s ability to turn the virus against itself is what makes it so interesting.
“We’re arming it with little molecular warheads that end up preventing it from infecting our cells; it’s our revenge on the virus.”
Lipton created and patented the medicine memantine in the 1990s for the treatment of neurological illnesses like Alzheimer’s, and he and his colleagues had been studying it for years prior to the COVID-19 outbreak. Memantine was originally an anti-influenza medication used in the 1960s, but after doctors found a woman’s Parkinson’s symptoms improved when she took the medication for the flu, they started looking into it for other disorders.
“My team had made these antiviral drugs better for the brain, and when COVID-19 emerged, we wondered whether we had also, in the process, made any of them better antivirals,” adds Lipton.
A library of compounds that were similar to memantine in general structure but covered with additional pharmacological warheads was put through a series of tests by Lipton and his team. They identified the drug candidate that they designated as NMT5 as having two key properties. First, it had the ability to recognize and attach itself to a pore on the surface of SARS-CoV-2. Second, it had the ability to chemically modify human ACE2 by employing a fragment of nitroglycerin as the warhead. The group realized that this could make the virus a way for it to kill itself.
In the new paper, Lipton’s team described NMT5 and tested it in both isolated cells and animals. They demonstrated how NMT5 firmly binds to SARS-CoV-2 virus particles as the viruses circulate within the body. Then, they described in detail how, if the medicine comes close enough to a particular molecule, it adds a chemical (similar to nitroglycerin). NMT5 adds a “nitro group” on the receptor when the virus is close enough to ACE2 to infect a cell. When ACE2 is changed in this way, its structure changes for about 12 hours, making it impossible for the SARS-CoV-2 virus to attach to it and cause an infection.
“What’s really beautiful is that this only knocks down availability of ACE2 locally when the virus is coming at it,” remarks Lipton. “It doesn’t knock down all the function of ACE2 elsewhere in the body, allowing for normal function of this protein.”
In tests done in cell cultures to see how well the Omicron variant of SARS-CoV-2 can attach to human ACE2 receptors, the drug stopped 95% of the virus from attaching. NMT5 significantly reduced COVID-19 viral levels in hamsters, eliminated blood vessel damage in the animals’ lungs, and reduced inflammation. The drug also demonstrated efficacy against over a dozen more COVID-19 variations, including the alpha, beta, gamma, and delta strains.
Most anti-viral drugs work by blocking a part of a virus directly. This can force the virus to change so that it can no longer be killed by the drug. The researchers believe that the medication will likely be successful against many more SARS-CoV-2 variations because NMT5 is simply using the virus as a carrier.
“We expect this compound would continue to be effective even as new variants emerge, because it doesn’t rely on attacking parts of the virus that commonly mutate,” adds first author Chang-ki Oh.
Although they have only tested the molecule in animal models, the team is now developing a version of the medicine for human testing while conducting more animal safety and efficacy experiments. This work is supported by a grant from the National Institutes of Health (U19 AI171443) to the Scripps Center for Antiviral Medicines & Pandemic Preparedness (CAMPP AViDD).
“These exciting findings suggest a new avenue for drug development that requires drug combinations for effective pandemic preparedness,” adds co-author Arnab Chatterjee, PhD.
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: This New Drug Can Actually Turn The COVID-19 Virus Against Itself
