The discovery of this new mutation could potentially help in the advancement of treatments for arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy.
A new mutation that causes arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM) has been identified by the UMC Utrecht in collaboration with the research group led by Eva van Rooij.
Scientists examined how this mutation affected cardiac muscle cells and learned something new about the disease’s underlying process.
This work, which was published today in Stem Cell Reports, may help pave the way for future therapies targeting ACM.
With the help of millions of working muscle cells, the heart is able to perform its vital pumping job. The ability of the individual cardiac muscle cells to interact with one another is crucial for ensuring that these contractions are carried out correctly.
So, it is essential that the cells that makeup heart muscle be in close proximity to one another. Desmosomes are complex protein structures that establish a bridge between heart cells and are present in a healthy heart.
Mutations in these genes may cause arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM).
ACM is a progressive disease that is often passed down through families in which the heart doesn’t contract properly. Even though 1 in 5000 people will get ACM at some point in their lives, there is still a lot we don’t know about the disease, and there are no effective ways to treat it.
Sebastiaan van Kampen, the study’s first author, explains that when his team examined the genetic makeup of an ACM patient, they discovered a previously unrecognized mutation in the desmoplakin gene.
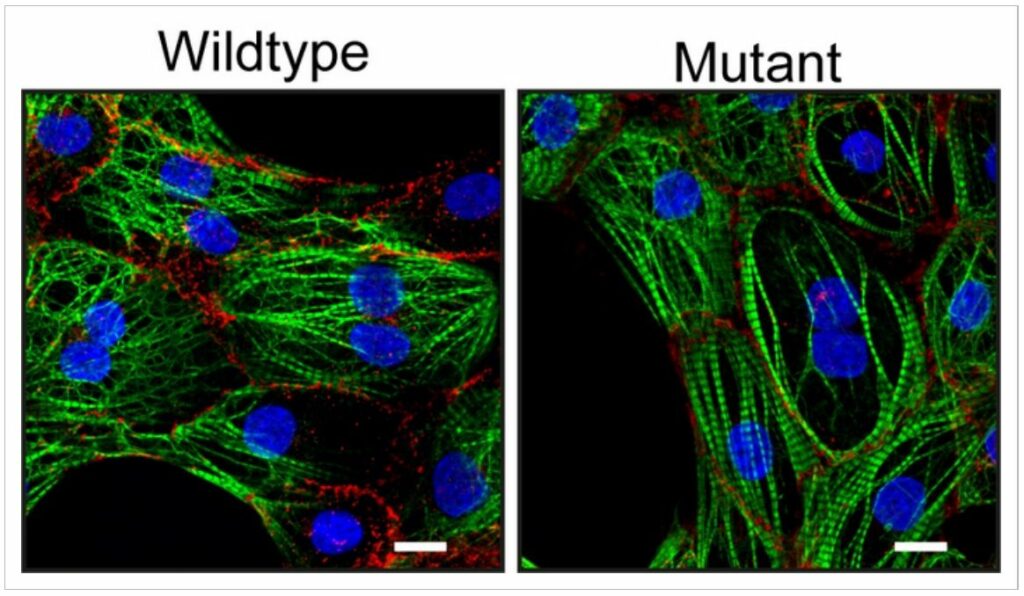
One of the genes involved in the development of desmosomes is called desmoplakin. Researchers grew heart muscle cells from the patient in the lab to find out what role this mutation played in the start of ACM.
“We compared these heart muscle cells to the same heart muscle cells in which we repaired the mutation using CRISPR/Cas9. The heart muscle cells that contained the mutation turned out to be less tightly connected,” the author adds.
The researchers also found that there are less ion channels in these cells. These channels are required for the action potential, a signal that causes contraction in cardiac muscle cells, to travel efficiently from one cell to the next. From this, they came to the conclusion that the new mutation can make patients get ACM.
ACM can be caused by more than one change. Still, not much is known about what causes the disease in the first place.
To fix this, the researchers used the patient’s heart muscle cells that had been grown in a lab as a model for the disease. They found that the “diseased” cardiac muscle cells had higher levels of the protein PITX2, which is also partially to blame for the loss of desmosomes and ion channels.
Van Kampen says, when they “removed the protein from the diseased heart muscle cells, the levels of ion channels and desmosomal proteins in the cells of the patient showed a remarkable recovery.”
So, the PITX2 protein is a big reason why the mutated heart muscle cells are changing.
“Although we don’t know how the new mutation leads to increased levels of PITX2, we see the same happening in a second mutation,” remarks last author Eva van Rooij.
“It’s possible that increased levels of PITX2 lead to ACM in the context of many more mutations.”
So, it is important to do more research on these different mutations.
Source: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2023.01.015
Image Credit: Jantine Monshouwer-Kloots, copyright Hubrecht Institute