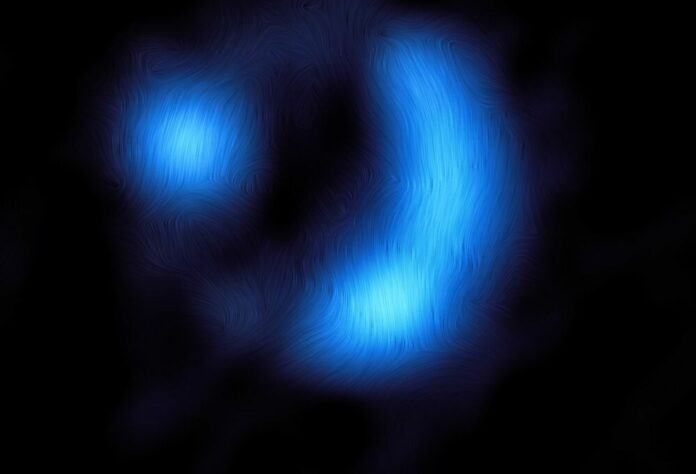
Magnetic Fields Are Not Just Local: ALMA Telescope Spots One 11 Billion Light-Years Away
Leveraging the capabilities of the Atacama Large Millimeter/Subsillimeter Array (ALMA), a team of scientists has successfully identified the magnetic properties of a galaxy so remote that it has taken over 11 billion years for its light to reach Earth.
This glimpse into a cosmic era when the Universe was a mere 2.5 billion years old offers valuable insights into the origins of magnetic fields in galaxies, including the Milky Way.
While it is common knowledge among astronomers that various celestial objects like planets, stars, and galaxies have magnetic fields, the general public may not fully grasp this.
James Geach, a leading astrophysicist at the University of Hertfordshire, UK, who spearheaded the study recently released in the journal Nature, notes, “Many people might not be aware that our entire galaxy and other galaxies are laced with magnetic fields, spanning tens of thousands of light-years.”
Enrique Lopez Rodriguez, a researcher at Stanford University, USA, who collaborated on this groundbreaking work, mentions, “We actually know very little about how these fields form, despite their being quite fundamental to how galaxies evolve.”
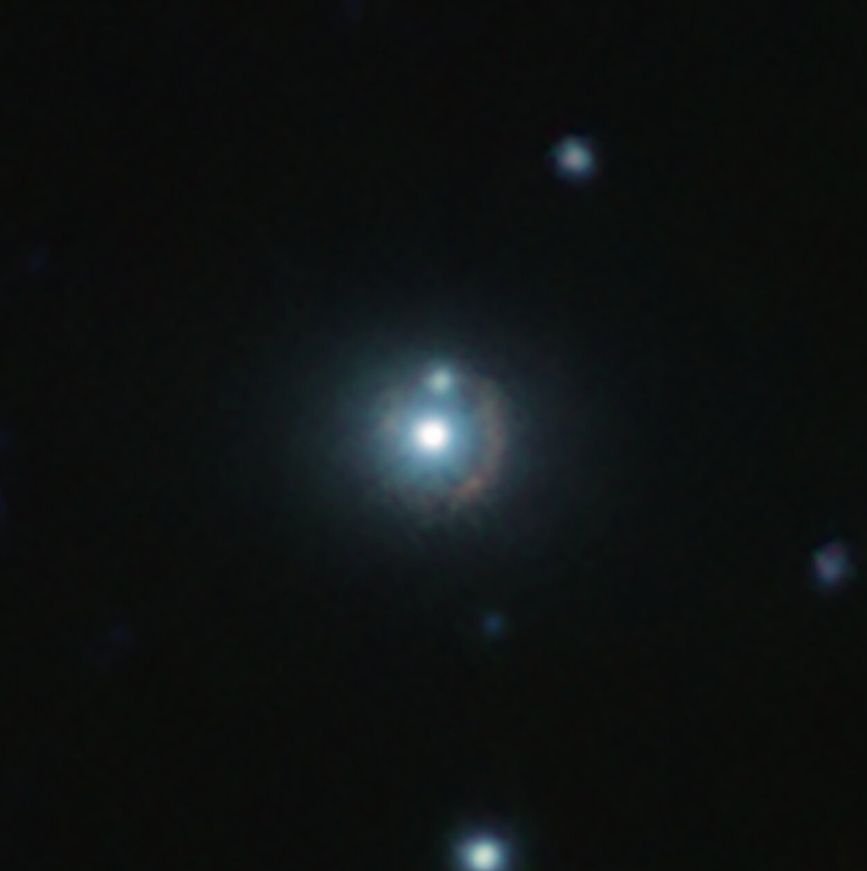

Prior to this study, astronomers had been limited to exploring the magnetic properties of galaxies closer to Earth.
Collaborating with the European Southern Observatory (ESO), Geach’s team discovered a fully mature magnetic field in a far-off galaxy, resembling the structure seen in galaxies that are much closer to us. The magnetic strength is a fraction of Earth’s—around 1,000 times weaker—yet it spans a staggering 16,000 light-years.
“This discovery gives us new clues as to how galactic-scale magnetic fields are formed,” says Geach. This revelation suggests that such extensive magnetic fields can materialize quickly during the formative stages of young galaxies.
The team speculates that vigorous star creation in the Universe’s infancy likely contributed to the swift genesis of these magnetic fields. Furthermore, these magnetic phenomena could, in turn, govern how subsequent stars come into existence.
ESO astronomer Rob Ivison, a co-author of the study, believes this observation opens “a new window onto the inner workings of galaxies, because the magnetic fields are linked to the material that is forming new stars.”
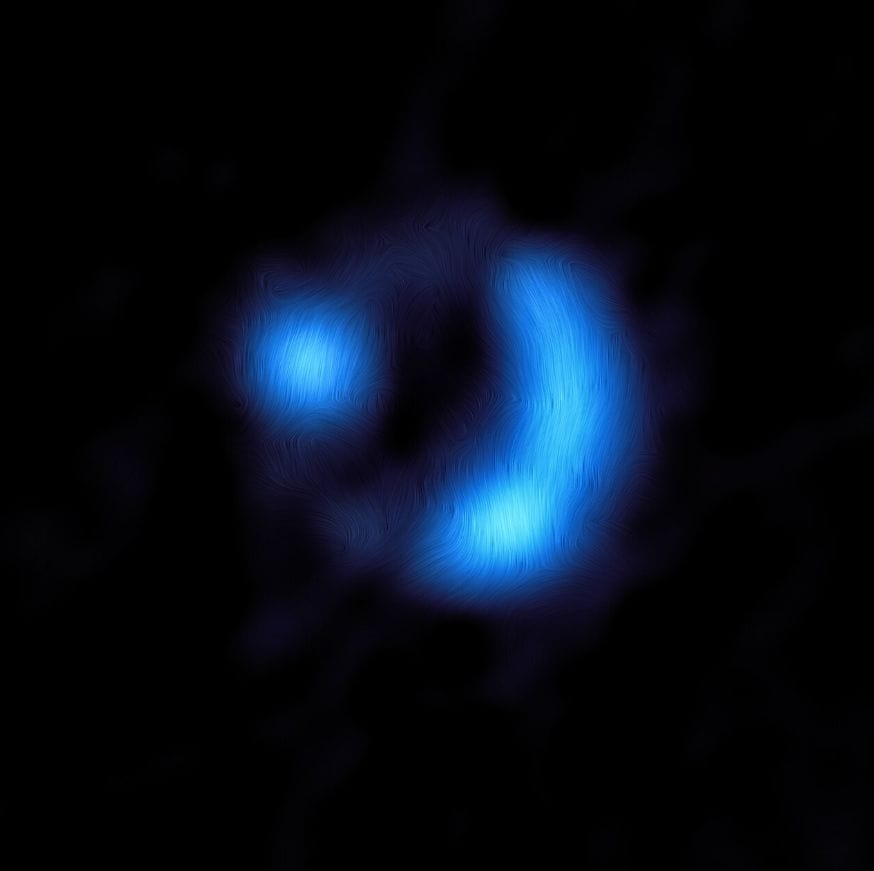
To confirm the existence of this magnetic field, the researchers studied light emitted by cosmic dust particles in a remote galaxy named 9io9. In the presence of a magnetic field, these dust grains align, causing the emitted light to polarize, or oscillate along a favored direction. ALMA’s detection of this polarized light signature from 9io9 marked the first-time verification of a magnetic field in a galaxy so far away.
“No other telescope could have achieved this,” asserts Geach. This landmark detection and future studies are expected to untangle the enigma surrounding the formation of these essential galactic features.
Source & Image Credit: ESO
