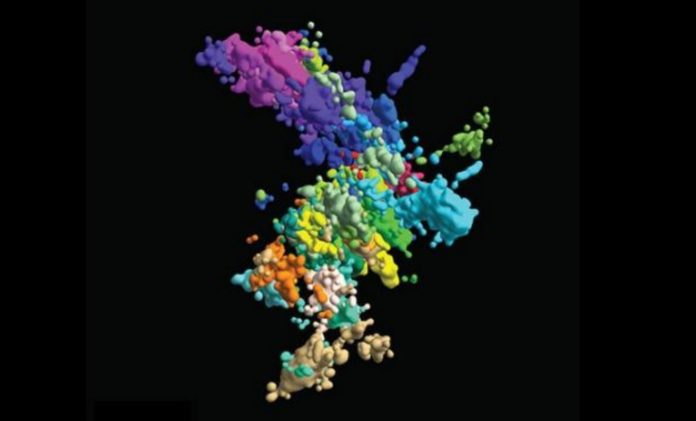
We are used to seeing chromosomes represented in the shape of an X, but this scheme may not be as exact as we thought. Researchers have created a three-dimensional image that shows what the chromosomes of our DNA really look like.
The typical X that represents chromosomes is made up of two chromatids that have joined together once DNA has replicated but before cell division is complete. Scientists point out that this representation is not as accurate.
“For 90 percent of the time, chromosomes don’t exist like that,” says physicist Jun-Han Su, a former Harvard University fellow and author of the study. So his team came up with a new way to represent the three-dimensional organization of chromatin in human cells, allowing for a more detailed understanding of how chromosome chemistry works.
To create the new high-resolution three-dimensional imaging system, the team put together a large number of snapshots of genomic loci – that is, of fixed chromosome positions – in order to get an accurate view of the DNA strands. This allowed obtaining a view never before achieved.
“It’s quite important to determine the 3D organisation to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the organisation and to also understand how this organisation regulates genome function”
explains the researcher of the study Xiaowei Zhuang.
The team is sharing their findings and progress so that other researchers can take their analysis further, and so that we can explore this invisible part of ourselves even more in the future. Perhaps the study of X-shaped chromosomes in high schools will soon be obsolete.
“We envision broad application of this high-throughput, multi-scale, and multi-modal imaging technology, which provides an integrated view of chromatin organisation in its native structural and functional context,” the team explained.