A group of physicists has investigated the properties of a space-time crystal created from magnons. According to the researchers, its capabilities could be applied in information technology.
Physicists have used quasiparticle magnons to form a new state of matter, called spacetime crystal, and have studied how matter interacts with other quasiparticles in this state. The research results were published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
- Brief Anger Hampers Blood Vessel Function Leading to Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke – New Study
- New Blood Test Pinpoints Future Stroke Risk – Study Identifies Inflammatory Molecules as Key Biomarker
- Enceladus: A Potential Haven for Extraterrestrial Life in its Hidden Ocean Depths
- New Experiment: Dark Matter Is Not As ‘DARK’ As All We Think
- Scientists in Fear of This New Predator From Red Sea Eating Native Species in Mediterranean
Scientists from Germany and Poland, led by Joachim Grafe of the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, discovered that when spin waves of electrons condense, they form a new exotic state of matter, which has a repeating pattern both in space as in time.
Just as the symmetry of space is broken in ordinary crystals, the space-time crystal is a changing physical system in which symmetry shifts, even with respect to time.
These structures, called space-time crystals or temporary crystals, were obtained for the first time experimentally in 2017.
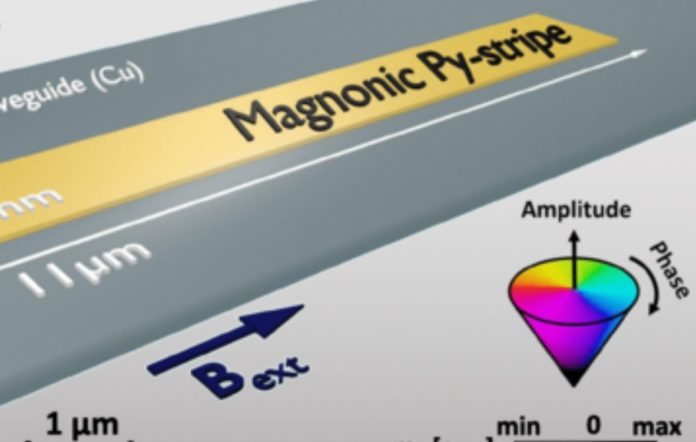
Grefe and his colleagues created their space-time crystal by applying a radio frequency field to a micrometer strip of nickel-iron alloy at room temperature.
The field excited the magnon that formed a dynamic spatial pattern. The authors compare it to the arrangement of the balls on a billiard table in the event that the billiard balls repeatedly returned to their original collective state after scattering.
The researchers studied the space-time crystal for its interaction with other magnons. When other quasiparticles were directed at the crystal, they were distributed in the same way as in the crystal itself. This scattering process produced ultrashort magnons, whose precise wavelengths could be adjusted by changing the parameters of the radio frequency field.
- Brief Anger Hampers Blood Vessel Function Leading to Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke – New Study
- New Blood Test Pinpoints Future Stroke Risk – Study Identifies Inflammatory Molecules as Key Biomarker
- Enceladus: A Potential Haven for Extraterrestrial Life in its Hidden Ocean Depths
- New Experiment: Dark Matter Is Not As ‘DARK’ As All We Think
- Scientists in Fear of This New Predator From Red Sea Eating Native Species in Mediterranean
The researchers say that the ability to easily reconfigure the space-time crystal, combined with its operation at room temperature, makes the device a suitable platform for magnon-based information technology.