A person in a state of lucid dream is able to perceive information and even answer questions using eye movements or facial muscles.
A group of scientists from France, Germany, the Netherlands and the United States managed to establish contact with people who were asleep and get feedback from them.
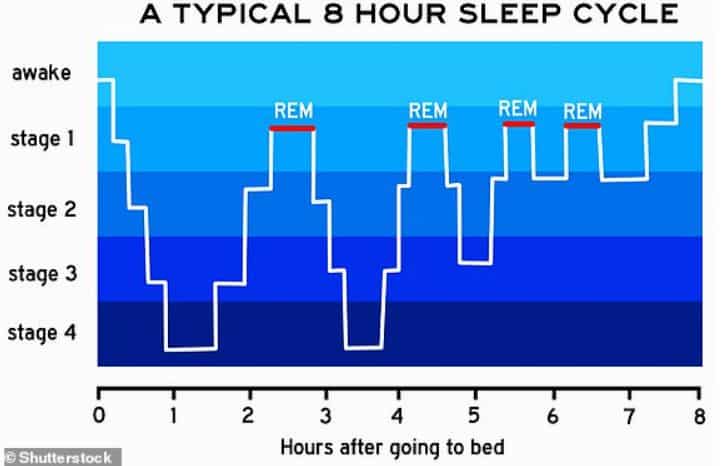
Experts have tested a procedure for two-way communication during lucid sleep – a state that occurs during the REM phase of sleep and is characterized by the understanding that a person is actually sleeping and does not experience everything that one sees and hears.
- Neuroscience Breakthrough: Study Pinpoints Brain Activity That Helps Prevent Us From Getting Lost
- Brief Anger Hampers Blood Vessel Function Leading to Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke – New Study
- New Blood Test Pinpoints Future Stroke Risk – Study Identifies Inflammatory Molecules as Key Biomarker
- Enceladus: A Potential Haven for Extraterrestrial Life in its Hidden Ocean Depths
- New Experiment: Dark Matter Is Not As ‘DARK’ As All We Think
Scientists have long wondered under what conditions lucid dreams arise and what experiences arise in such a state.
In four parallel experiments, the brain activity was monitored in 36 people who frequently had lucid dreams.
During the experiments, scientists tried to “reach out” to a sleeping person, transmitting information in various ways: from a simple audio recording of a question to a text that was transmitted in the form of flashes of light or touches of a volunteer’s body.
The observations and stories of the participants in the experiments confirmed that the volunteers heard or saw the questions and tried to answer them both in dreams and in reality. Some of the study participants learned to answer monosyllabic questions using eye movements or facial muscles.
Scientists obtained similar results in all experimental groups, despite the differences in observation methods and participants.
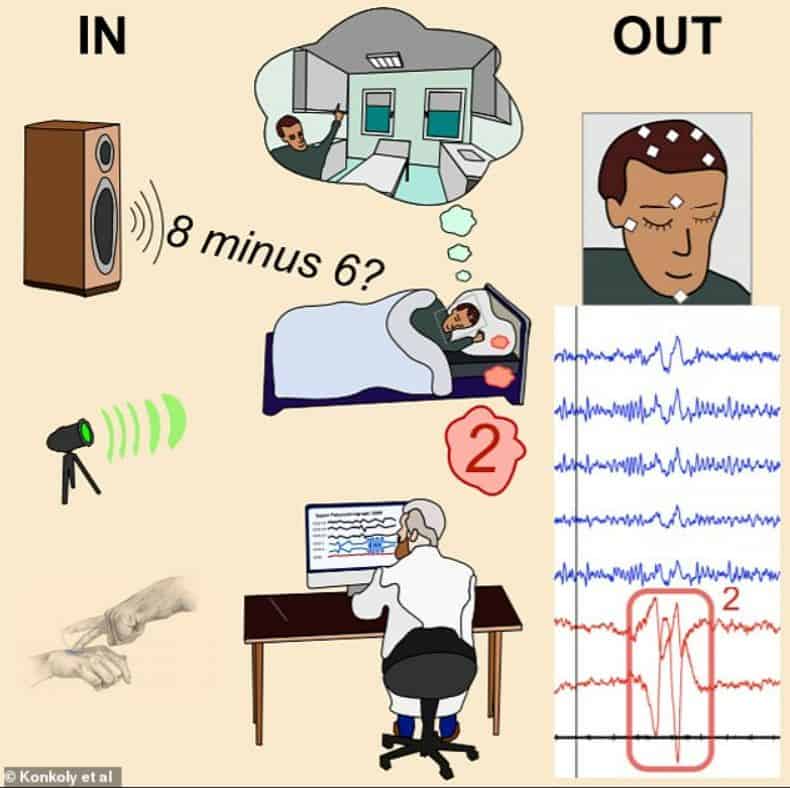
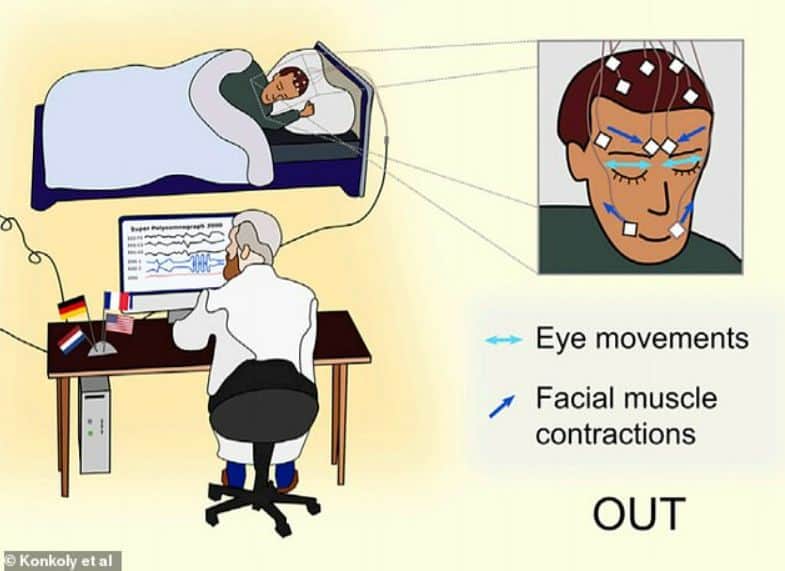
The authors of the study believe that during lucid dreams, a person continues to interact with the outside world and this can be used to study them.
The research results were published in the journal Current Biology.
