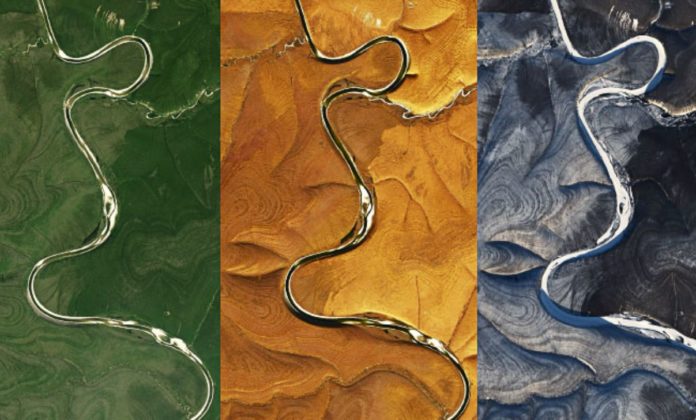
A peculiar and beautiful image became a scientific detective story and an unsolved case for NASA.
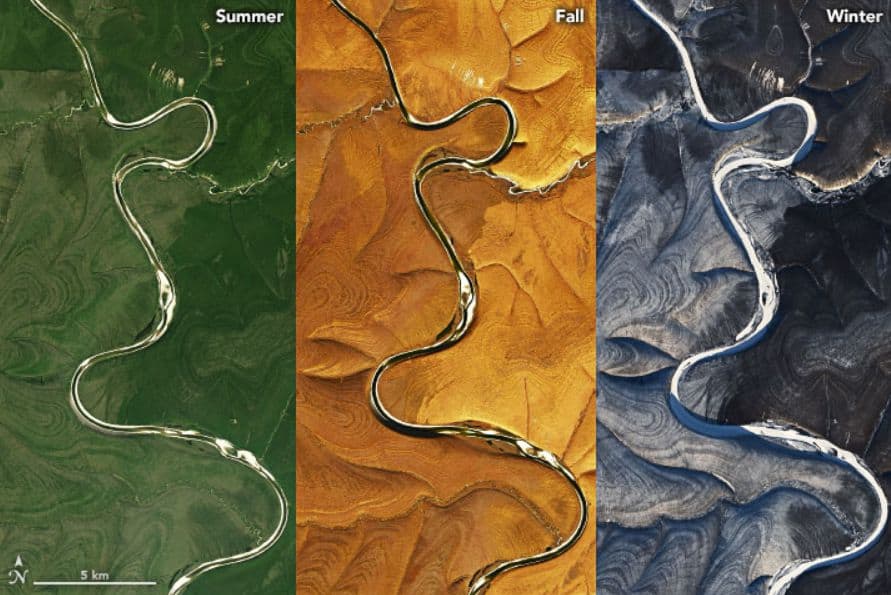
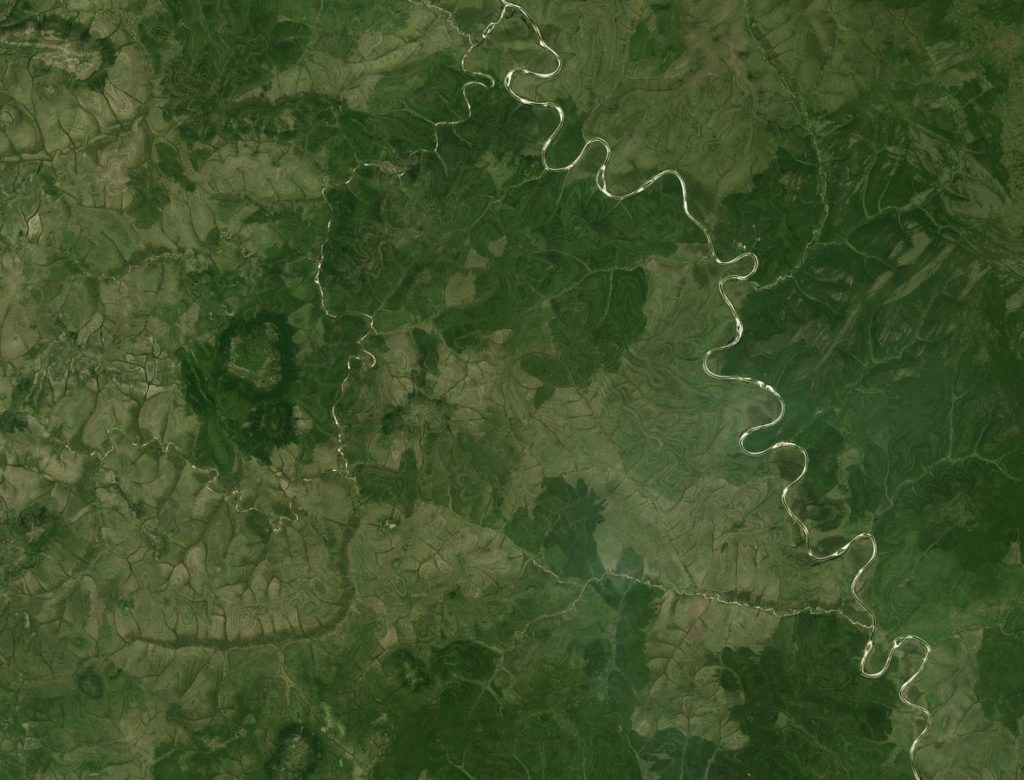
In images captured by the Landsat 8 satellite’s Operational Land Imager (OLI), striped patterns twist and rotate around the hills of the northern plateau of central Siberia. They disappear at lower elevations and latitudes.
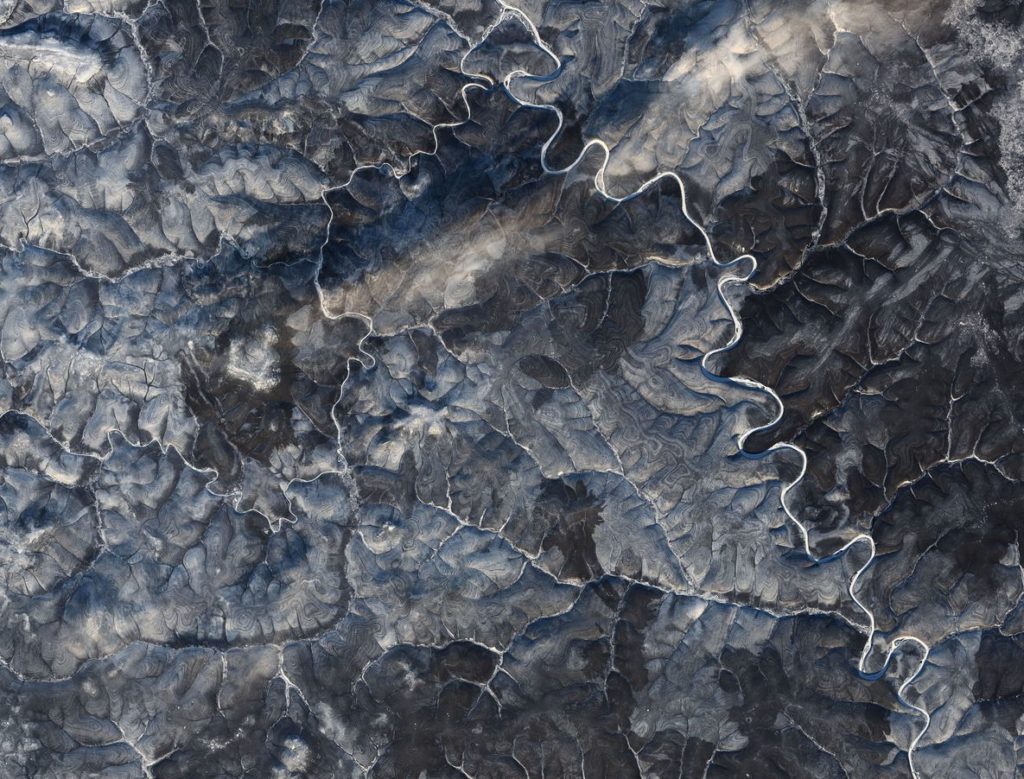
The pattern is most evident in the northern winter when the whiteness of the snow makes the contrast in the landscape texture much more marked.
According to NASA, These could be several possible causes for this distinctive stripe pattern.
- Brief Anger Hampers Blood Vessel Function Leading to Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke – New Study
- New Blood Test Pinpoints Future Stroke Risk – Study Identifies Inflammatory Molecules as Key Biomarker
- Enceladus: A Potential Haven for Extraterrestrial Life in its Hidden Ocean Depths
- New Experiment: Dark Matter Is Not As ‘DARK’ As All We Think
- Scientists in Fear of This New Predator From Red Sea Eating Native Species in Mediterranean
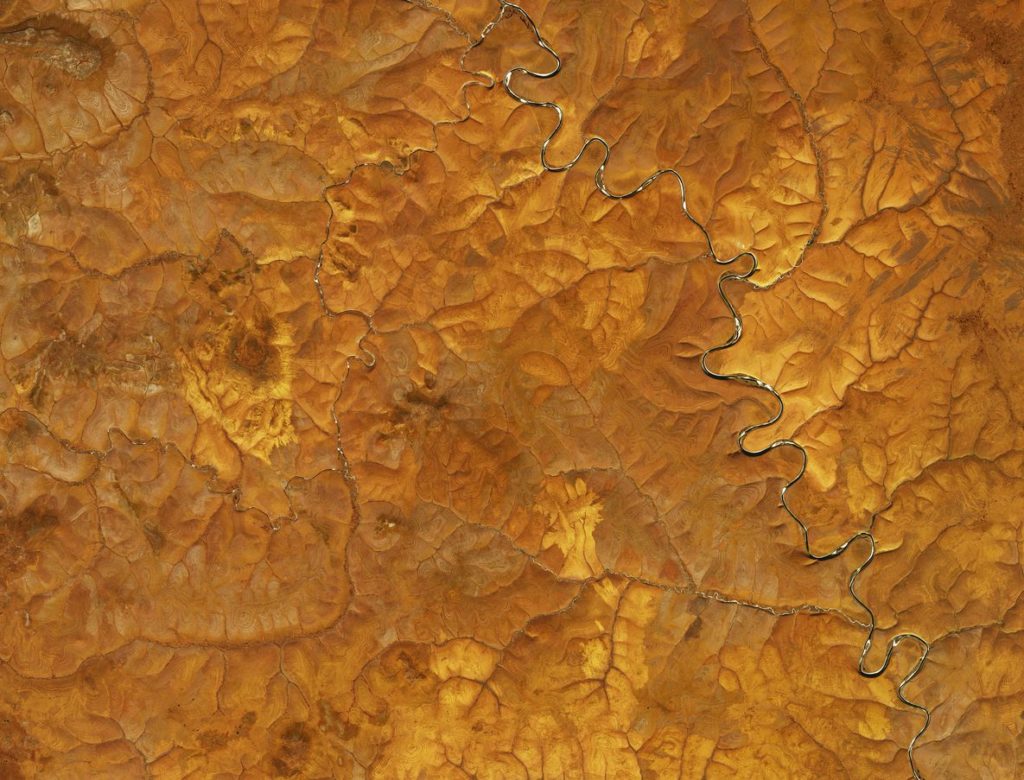
1. One of the suggested explanations for the phenomenon lies in the inherent geological features. According to the space agency, this region of the central Siberian plateau lies within the Arctic Circle and is covered in permafrost for most of the year, although occasionally – but briefly – it thaws.
Freeze-thaw cycles are known to create patterns of polygons, circles, and stripes on the surface. The pattern occurs when soil and stones naturally arrange themselves during freeze-thaw intervals.
However, studies have shown that these types of stripes tend to occur on a much smaller scale and tend to be oriented downward.
2. For geomorphologists, the nature of the soil offers another explanation for the stripes. In such cold regions, the soil can become gelisols, that is, soils with permafrost in its upper two meters and often with darker and lighter layers that are distinguished by having more organic matter or minerals and sediments.
As the soil freezes and thaws, the layers break down and mix vertically in a process called cryoturbation. Persistent freeze-thaw action throughout the seasons can cause the layers to line up in a striped pattern.
The tundra vegetation may grow in these layers preferably of gelisol accentuating stripes seen from above. However, this hypothesis has not been proven on a large scale.
3. It could be due to erosion, according to scientists. Thomas Crafford, a geologist with the US Geological Survey, told NASA that the stripes resemble a pattern in sedimentary rocks commonly known as layer geology. These patterns occur when snowmelt or rain drifts downhill, cutting and dragging chunks of sedimentary rock in piles. This erosion can cause a staggered pattern that appears as streaks from space, similar to a slice of layer cake, with the darker stripes representing steeper tracts of land, while the lighter stripes denoting flatter areas, Crafford explained.



- Brief Anger Hampers Blood Vessel Function Leading to Increased Risk of Heart Disease and Stroke – New Study
- New Blood Test Pinpoints Future Stroke Risk – Study Identifies Inflammatory Molecules as Key Biomarker
- Enceladus: A Potential Haven for Extraterrestrial Life in its Hidden Ocean Depths
- New Experiment: Dark Matter Is Not As ‘DARK’ As All We Think
- Scientists in Fear of This New Predator From Red Sea Eating Native Species in Mediterranean
“The horizontal stripes appear to be different layers of sedimentary rock,” said Walt Meier, an ice specialist at the US National Snow and Ice Data Center.
“The shape of the erosion pattern looks a bit different than standard sedimentary erosion, but my opinion is that it is due to permafrost. Rivers are eroding through frozen soil. There could also be some effect of frost affecting topography,” he added.
Several rivers run through the plateau, including the Marja, and as the stripe pattern approaches the river, it begins to fade. This could be the result of sediment accumulation along the banks of the river due to millions of years of erosion, expressed NASA.
