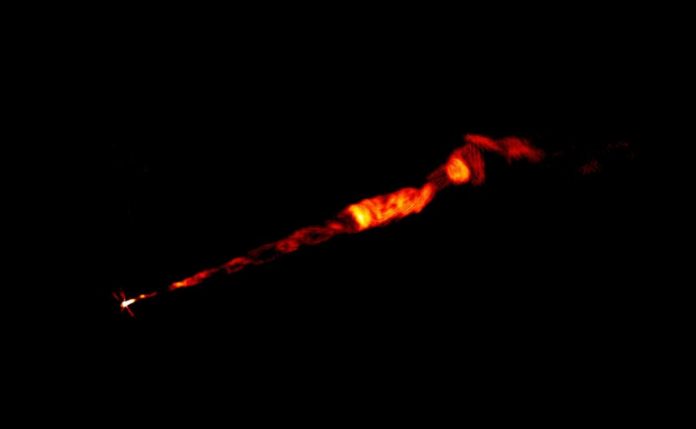
It is the first time this structure has been seen at such a great distance from the black hole, thanks to the magnetic field.
When the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) took a picture of the supermassive black hole at the heart of the galaxy M87 in 2019, it made the galaxy famous. A jet of the material comes out of the center of M87, and it travels almost at the speed of light and extends far beyond the galaxy itself. This is a lot bigger than our Milky Way.
Now, an international group of scientists has seen how this jet is directed by a magnetic field and forms a double helix shape.
The Karl G. Jansky Very Large Array (VLA) radio interferometer from the United States National Radio Astronomy Observatory helped make this discovery possible.
The images indicated that the magnetic field retains its helical structure up to 3,300 light years away from the supermassive black hole. Although these magnetic field arrangements have previously been identified in other galaxies, they had never been observed at such great distances from the central black hole.
“We obtained very high-quality images at various wavelengths of the M87 galaxy using the VLA, and that allowed us to reconstruct the three-dimensional structure of the jet’s magnetic field for the first time,” said Alice Pasetto.
“The material of this jet traces a double helix, a structure very similar to the DNA molecule ”.
M87 is an elliptical galaxy 55 million light-years away from Earth. Its supermassive black hole, with a mass of around 6.5 billion times that of the Sun, is one of the most well-known examples of this type. Not only did the EHT get the first photograph of it, but new images released earlier this year revealed the magnetic field near the black hole’s event horizon.
Pasetto and his colleagues used the VLA to analyze the magnetic field’s features on a broad scale by studying light polarization in radio. This feature of light is precisely tied to the direction of the magnetic field where it was emitted, and they were able to map the magnetic field along the jet with previously unheard-of precision. They employed the VLA in its most extended configuration to capture the best resolution photos of this galaxy’s jet yet recorded.
“We expect the magnetic field to adopt a helical configuration very close to the black hole, and we think that in fact this configuration is what allows the material to be channeled out in a very narrow jet. But we did not expect to find that this helical configuration remains at such a distance from the center of the galaxy,” added José Luis Gómez, a researcher at the Institute of Astrophysics of Andalusia (IAA-CSIC) who is participating in the work.
The magnetic field should weaken increasing distance from the black hole, resulting in the loss of the initial helical structure. However, the research team believes that in this instance, instabilities in the jet can rearrange the magnetic field and keep the structure intact over very long distances. These instabilities cause high-pressure zones in the material, compressing the magnetic field lines and increasing their strength.
The findings show that the observed double helix structure is the result of an interaction between instabilities in the jet and the magnetic field.
“If this happens in M87, it is possible that it also happens in other similar jets driven by other galaxies,” said Carlos Carrasco González, radio astronomer at UNAM who is participating in the work.
“M87 is a galaxy relatively close to us and its jet is very powerful, making it an ideal object for detailed study. Their study helps us understand the phenomenon of relativistic jets, which is present in many astronomical objects in the universe, not only active galaxies.”
Source: The Astrophysical Journal Letters
Image Credit: Pasetto et al., Sophia Dagnello, NRAO / AUI / NSF
You were reading: Scientists find a double helix in the jet emanating from M87’s black hole