This is the first CRISPR protein that has been shown to have the potential to enable at-home testing for several deadly viruses, including COVID-19, influenza, Ebola, and Zika.
A new CRISPR protein has been discovered that can break down single-stranded RNA, single-stranded DNA, and double-stranded DNA in bacteria. This is the first time that CRISPR has been able to perform this function.
The new CRISPR protein has the potential to be used in the creation of inexpensive, highly sensitive at-home diagnostic tests for various infectious diseases such as COVID-19, influenza, Ebola, and Zika, according to a study published in the journal Nature. The protein’s ability to target various types of genetic material makes it a promising tool for these types of tests.
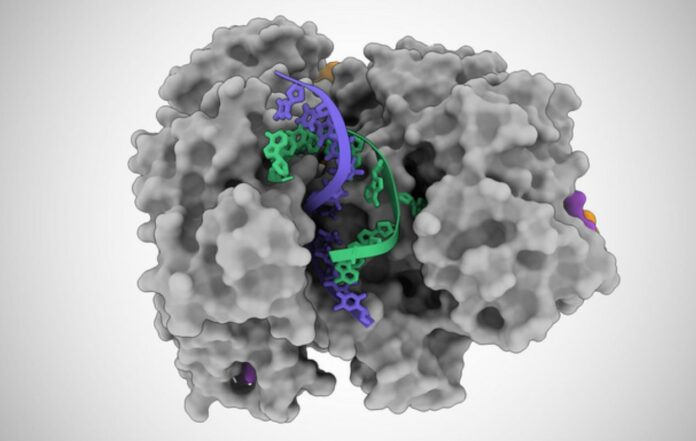
The research team used cryo-EM, a high-resolution imaging technique, to observe how the Cas12a2 protein functions. They found that when it binds to a specific sequence of viral genetic material (called target RNA), a section of the protein extends outward to reveal an active site, similar to a switchblade knife being opened.
After the active site is revealed, it begins to cut any genetic material it encounters. However, the researchers found that by making a single change to the Cas12a2 protein, the active site can be made to specifically break down single-stranded DNA. This ability could be valuable in the development of diagnostic tests for a variety of viruses.
This technology has the potential to create diagnostic tests that combine the benefits of PCR-based tests (high sensitivity, high accuracy, and the ability to detect active infections) with the advantages of rapid at-home tests (low cost and no need for specialized lab equipment). It could also be easily modified for use with any new RNA virus.
“If some new virus comes out tomorrow,” says co-corresponding author David Taylor, “all you have to do is figure out its genome and then change the guide RNA in your test, and you’d have a test against it.”
To use this diagnostic, patients would need to provide a saliva or nasal sample, which would be mixed with the modified Cas12a2 protein, a piece of guide RNA that identifies a specific virus, and a fluorescent probe that signals when single-stranded DNA has been cut. It would still require additional development before it could be used.
The term “CRISPR” refers to a collection of tools that are found naturally in bacteria and have been modified by researchers for use in gene editing. It is the first time that a CRISPR protein has been discovered to be able to destroy such a large variety of genetic material.
“Cas12a2 basically grabs the two ends of the DNA double helix and bends it really tightly,” adds co-author Jack Bravo. “And so, the helix in the middle pops open, and then this allows this active site to destroy the bits of DNA that become single-stranded. This is what makes Cas12a2 different from all the other DNA-targeting systems.”
Source: 10.1038/s41586-022-05560-w
Image Credit: Jack Bravo/University of Texas at Austin