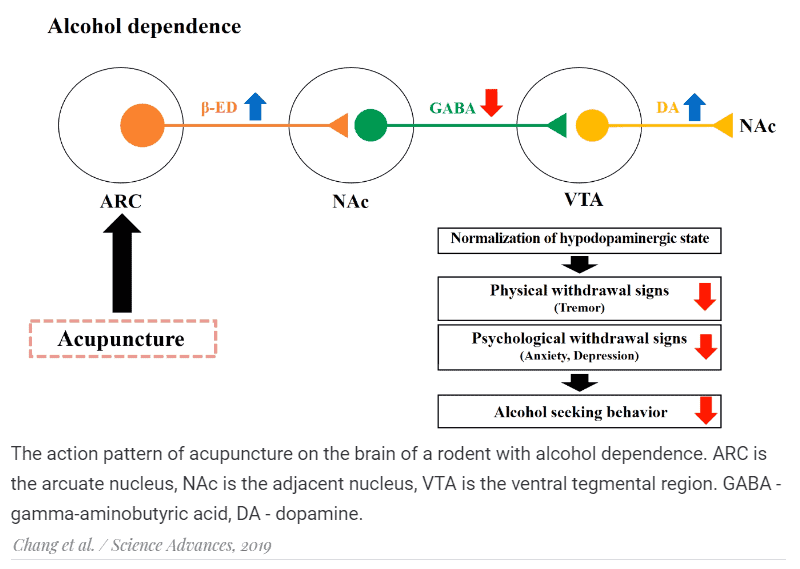
The physical dependence on alcohol in rats (the method has not yet been tested on other animals) can be weakened by introducing an acupuncture needle at a specific point on the forelimb, according to Science Advances. Apparently, acupuncture in this case enhances the production of beta-endorphin in the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, from where this substance enters the adjacent nucleus, and it already determines the reaction to stress from the lack of alcohol.
Dependence on ethanol is mental and physical, the second comes after the first and, fortunately, not all alcohol consumers reach it. A person suffering from physical dependence must always have ethanol in his body, otherwise, in addition to increased anxiety and depression, tremors of limbs and convulsions begin, as well as some other unpleasant symptoms.
Alcoholism, in principle, can occur in a wide variety of animals. The reactions described above were also recorded in rats, which scientists have accustomed to the constant use of alcohol. Therefore, the mechanisms and consequences of alcoholism, as well as methods for its treatment, are often studied in these animals. Researchers at Wake Forest Baptist Medical Center (USA) and several South Korean research institutions led by Chae Ha Yang from Daegu Haani University have used rats to test the effectiveness of acupuncture for physical dependence on alcohol.
Animals were given ethanol for 16 consecutive days, and at the end of this period, an acupuncture needle was inserted for 20 minutes at one of two points on the wrist – HT17 (Shen-Men) or located near LI5. The animals of the control group were not injected with needles. Two points were tested in order to understand whether there are differences in the effects of exposure to them and whether acupuncture has any nonspecific effect on the body of rodents (the authors note that stimulation of any point can cause movement disorders or convulsions).
After that, the animals were placed in a labyrinth, where part of the sleeves had an upper wall (it was dark inside), and part was open on top. It is believed that the higher the animal’s anxiety, the more time it spends in the arms closed from the light. Those rats exposed to HT17 showed much less anxiety than animals from the other groups. Convulsions were not observed in these animals, and tremor, which was additionally provoked by harmaline, was significantly weaker than in the remaining rats. The effect of HT17 stimulation on tremor was associated precisely with alcoholism, since rodents that never took alcohol but were under the influence of harmaline, acupuncture did not help relieve tremor.
In addition, scientists have described the possible mechanism of action of the acupuncture point HT17. Acupuncture is thought to alleviate pain due to effects on the endorphinergic systems of the brain, causing the release of beta-endorphin, a substance with an analgesic effect. The same substance causes pleasure, and its concentration in the brain with alcoholism is significantly reduced. In a new series of experiments, rats with a physical dependence on alcohol were injected with 0.25 or 0.5 micrograms of beta-endorphin in each nucleus accumbens (this is a paired structure) instead of an acupuncture session. In this case, the behavioral and neurological symptoms of physical dependence on alcohol also weakened, and the higher the concentration of beta-endorphin, the more pronounced the effect.
Finally, rats with an addiction to alcohol, who were trained to get their own ethanol using a lever, after an acupuncture session, as well as after the introduction of beta-endorphin into the adjacent nuclei, were much less likely to take the opportunity to pour a ten percent alcohol solution into their drinkers. This means that acupuncture reduces the craving for alcohol itself, and not only alleviates the symptoms of ethanol dependence.
The adjacent nucleus itself does not produce beta-endorphin. Therefore, the authors suggest that acupuncture acts on the arcuate nucleus of the hypothalamus, and already it produces the corresponding substance and directs it to the adjacent nucleus. This assumption is confirmed by the fact that neurons of the arcuate nucleus capable of producing endorphins were activated in rats with alcohol dependence after acupuncture, judging by the intensity of c-fos gene expression in them.
It should be noted that the experimental and control groups in all series of experiments contained only five to nine animals. These are very small samples, and the effects that appear on them may differ from those that are visible when considering a larger (at least tens and hundreds) number of repetitions. However, the small size of the groups did not cause a sharp rejection among the reviewers of the article and it was published. The question also arises as to how the authors determined the position of points on another type of animal, because their system was originally designed for humans.
However, this is not the first work in a peer-reviewed journal, which shows the therapeutic effects of techniques from the arsenal of traditional medicine. So, in 2016, the US National Institutes of Health published a meta-analysis of many studies on the effectiveness of non-traditional methods of treating pain of various kinds. It, among other things, concludes that acupuncture reduces the intensity of pain in the back and knee joint.