In a recent study, the US scientists used a colloidal solution of cadmium selenide sensitive quantum dots that were sensitive to visible light to catalyze the reaction to produce cyclobutane derivatives, one of the structural elements of biologically active substances. The reagents were coordinated on the surface of quantum dots, which transferred energy to them for interaction so that 98 per cent of the substance obtained during the reaction had a given position of atoms in space.
The photochemical cycloaddition reactions, during which biologically active four-substituted cyclobutane fragments are formed, can go through the formation of a triplet transition state. It lives long enough for the reaction to pass and can be formed by triplet-triplet energy transmission, for example, from a complex compound of a transition metal or organic chromophore.
The quantum dots, a few nanometer-sized particles, can also transmit energy. They are so small that quantum effects become significant in them, and their optical and electronic properties become similar to the properties of a molecule.
The distances between stationary energy levels, as well as the radiation energy of quantum dots, can be adjusted by changing their size. So, having selected up to the tenth nanometer the necessary geometric parameters of the dots, Yishu Jiang and his colleagues from Northwestern University successfully carried out a series of selective photochemical cycloaddition reactions catalyzed by a colloidal solution of quantum dots from cadmium selenide. Molecules in a certain way (regio- and stereoselectively) were sorbed on the surface of quantum dots that absorbed the photon of the incident light, which transferred the energy necessary for the formation of chemical bonds.
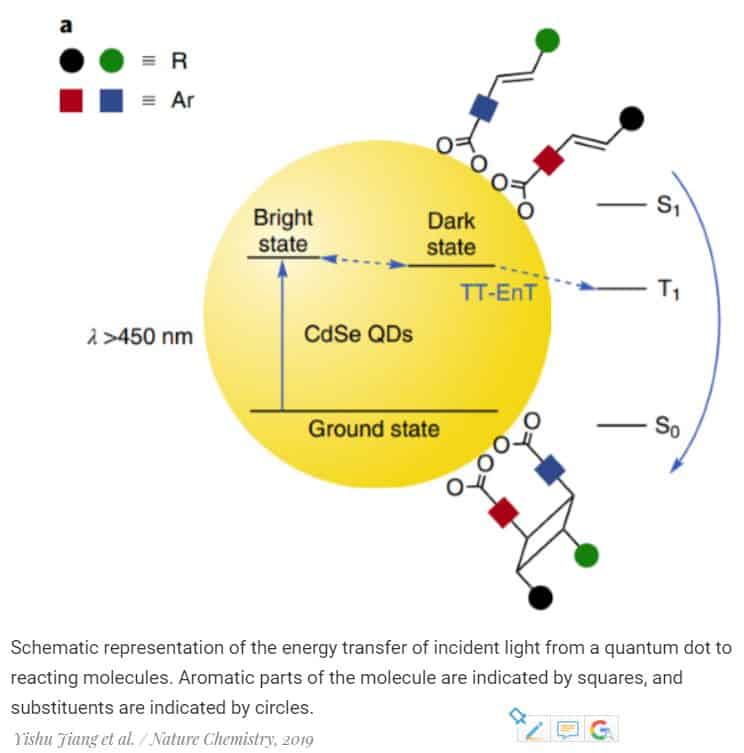
During 48-hour reaction cycles, the quantum dots did not break down, did not aggregate, and did not lose catalytic activity. For synthesis, it is necessary to transfer energy, without the addition of a solution of particles of cadmium selenide and without exposure to light, the reaction did not pass.
To improve the sorption of reacting molecules on the surface of the catalyst, the authors modified one of the ends of the reagent with a carboxyl group. The yield of the reaction involving molecules without terminal carboxyl groups was more than ten times lower. And the most regioselectively reacted molecules had aromatic substituents at the opposite end.
Comparing the new method with the synthesis in the presence of organometallic catalysts, the researchers noticed that when using quantum dots, the reaction proceeds several times more selectively, and the result is a previously inaccessible stereoisomer.
According to the authors, quantum dots make it possible to control the configuration of the obtained cyclobutane derivatives, even if it is not beneficial during the reaction for interacting molecules. Moreover, scientists suggest that such a catalyst can accelerate any reaction in which the formation of an excited triplet state is necessary, as in the studied cycloaddition reaction.
It is very important to use quantum dots of a certain diameter because the course of the reaction depends on this. Two years ago, American scientists studied in detail the mechanism of the formation of quantum dots from cadmium selenide to provide control over their synthesis and increase the reproducibility of the reactions of their production.