Captivating Close-Ups Show Amazing Details Hiding in Neptune’s Atmosphere
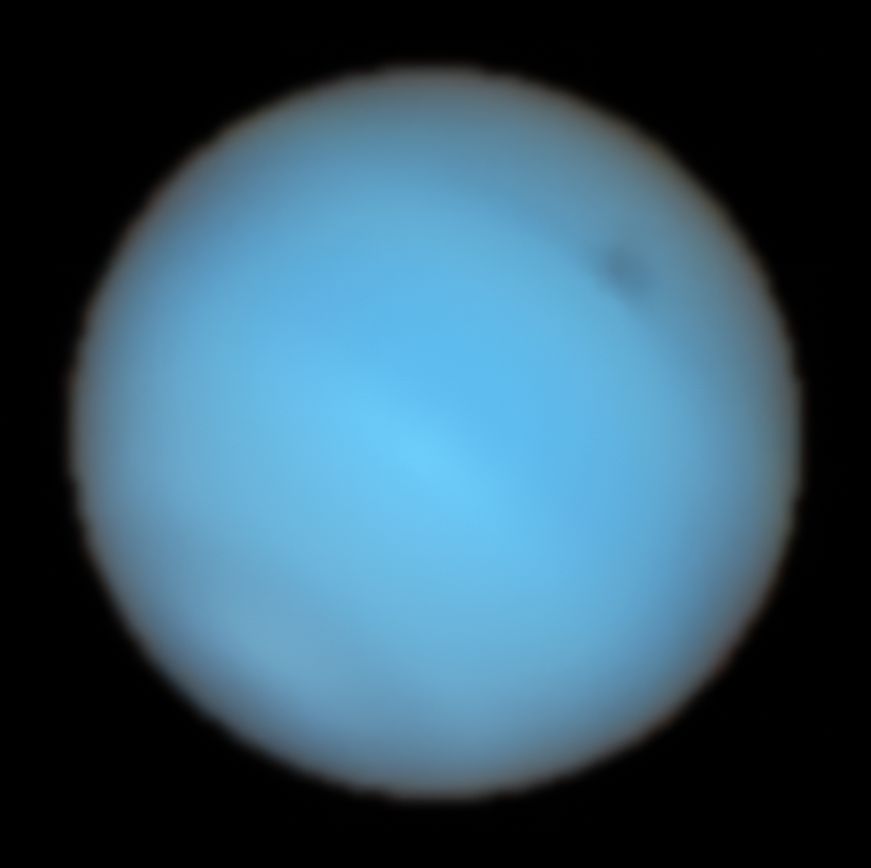
With the help of ESO’s Very Large Telescope (VLT), sky-gazers have identified a prominent shadowy mark on Neptune, as well as an unexpectedly modest brilliant spot nearby. This is a pioneering discovery, marking the first observation of Neptune’s dark mark using an Earth-based telescope.
Astronomers have been puzzled by these sporadic structures in Neptune’s atmosphere, and the latest findings provide further light on their nature and origin.
Majestic planets often sport vast marks in their atmospheres, with Jupiter’s Great Red Spot being the most iconic. Neptune first revealed its dark mark to NASA’s Voyager 2 in 1989, but it vanished after a short period.
Patrick Irwin, an academic at the University of Oxford in the UK and the primary researcher of the investigation presented today in Nature Astronomy, expressed, “Since the first discovery of a dark spot, I’ve always wondered what these short-lived and elusive dark features are.”

Drawing on the VLT data, Irwin’s group dismissed the notion that these marks resulted from cloud gaps. Instead, their analysis suggests these shadowy regions possibly originate from atmospheric particles getting tinted in a stratum beneath the primary visible haze as the planet’s icy mists and hazes intertwine.
Understanding this was quite challenging given the transitory nature of these marks in Neptune’s skies.
These dark areas aren’t permanent residents of Neptune’s atmospheric tapestry, and detailed analysis of them had been elusive. An opening emerged when the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope spotted multiple shadowy regions on Neptune, including a 2018 discovery in its northern territory. Seizing this chance, Irwin’s team employed ground tools adept for this intricate scrutiny.
Leveraging the VLT’s Multi Unit Spectroscopic Explorer (MUSE), they dissected the sunlight bouncing off Neptune, producing a 3D spectrum. This advanced technique allowed a more nuanced study of the mark.
Irwin remarked, “I’m absolutely thrilled to have been able to not only make the first detection of a dark spot from the ground, but also record for the very first time a reflection spectrum of such a feature.”
By examining different color wavelengths that penetrate varying atmospheric depths, the researchers could discern the spot’s position within Neptune’s atmosphere. The color profile also shed light on the atmospheric layers’ chemical make-up, hinting at why the mark appeared shaded.
Interestingly, another revelation was in store. Michael Wong, a co-author of the study from the University of California, Berkeley, USA, noted, “In the process, we discovered a rare deep bright cloud type that had never been identified before, even from space.”
This unique cloud formation mirrored the altitude of the primary mark, marking it distinct from earlier observed companion clouds.
The prowess of ESO’s VLT now empowers astronomers to decode celestial mysteries like Neptune’s spots right from Earth.
Wong added: “This is an astounding increase in humanity’s ability to observe the cosmos. At first, we could only detect these spots by sending a spacecraft there, like Voyager. Then we gained the ability to make them out remotely with Hubble. Finally, technology has advanced to enable this from the ground.
Wong jokingly added: “This could put me out of work as a Hubble observer!”
Image Credit: Shutterstock & ESO
