More Than Just Climate: New Study Shows We’ve Overstepped 6 Vital Environmental Limits
A recent research update on Earth’s sustainability framework reveals escalating human activities are jeopardizing our planet, amplifying the potential for catastrophic shifts in Earth’s equilibrium.
For millennia, the symbiotic relationship between life (signified by the Biosphere Integrity, a core planetary boundary) and our planet’s climate has steered Earth’s environmental status. However, human interventions—such as land repurposing, altering water distribution in rivers and land, the release of man-made chemicals, and greenhouse gas emissions—are influencing these age-old processes.
It’s paramount we respect and sustain Earth’s natural processes, akin to those that have guided its conditions for approximately the past 12,000 years. Such maintenance is vital to prevent radical environmental changes that could undermine the Earth’s capacity to nurture contemporary societies.
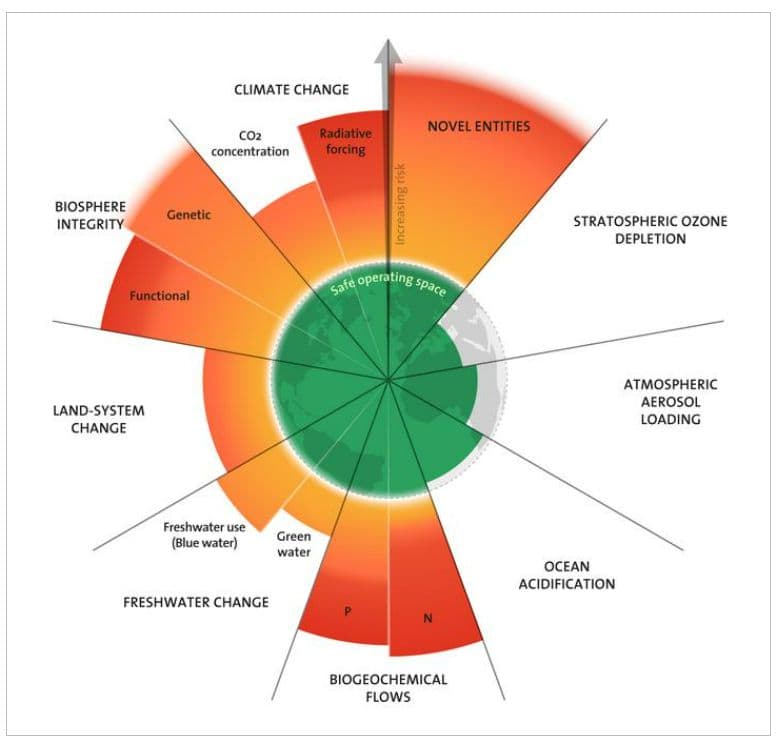
These “planetary boundaries” signify Earth’s vital components that ensure stability and habitability for humanity. The intrusion into these safety thresholds is predominantly due to human activities impacting these vital elements. This research framework employs cutting-edge scientific knowledge about Earth’s operations to designate a “green zone” for human existence. This involves outlining boundaries to human-induced influences to circumvent potentially irreversible damage to the environment we rely upon.
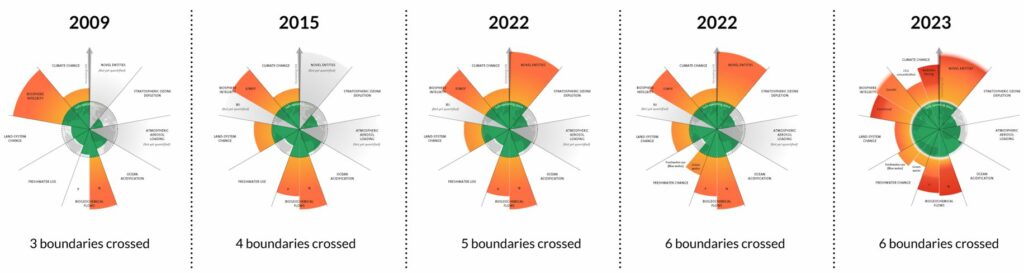
This groundbreaking study presents measurements for each boundary. Alarmingly, we’ve overstepped in six areas. All, with the sole exception of the Earth’s ozone layer, are seeing escalating levels of threat. A sole concentration on climate change isn’t sufficient. The immediate development of Earth-centric models, particularly focusing on the interplay between Climate and Biosphere Integrity, is imperative.
Published in Science Advances, this research marks the third revision of the framework, a collaborative effort by twenty-nine global scientists.
Earth’s “Blood Pressure” is rising
Katherine Richardson, a renowned professor at the Globe Institute and the head of the Sustainability Science Centre at the University of Copenhagen, emphasizes the alarming overstepping of our planetary limits:
- Breaching six of these thresholds doesn’t directly spell catastrophe, but it’s undoubtedly a red alert. It’s akin to our health metrics, like blood pressure. Consistently high readings may not instantly lead to a health crisis, but they amplify the risks. Thus, for the future of us and subsequent generations, it’s crucial we mitigate the strain on these six crucial planetary markers.
The study underscores the significance of understanding the intricate interplay between these boundaries:
- Solely addressing the aftermath of human-induced climate alterations won’t suffice to shield our planetary ecosystem from irrevocable damage, highlights Johan Rockström, the spearhead of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and the visionary behind the 2009 framework.
- Alongside climate considerations, safeguarding the biosphere’s integrity is paramount to Earth’s stability. Our findings emphasize that countering global warming and preserving a robust biosphere are two sides of the same coin,” asserts Wolfgang Lucht, the principal analyst at PIK’s Earth System Analysis division.
Biomass Consumption and Biodiversity
Prioritizing the ‘Land Use Change’ threshold highlights the growing global reliance on biomass, replacing traditional fossil fuels like coal, oil, and gas. Biomass emerges from photosynthesis, where sunlight is harnessed by plants and converted into energy, which in turn supports the diverse spectrum of life.
Richardson remarks, “Our study shows that humans are appropriating the equivalent of ~30 % of the energy that was available to support biodiversity before the Industrial Revolution.”
“Surely, the removal of so much of the energy that otherwise would have been available to nature must be a driver of biodiversity loss. Therefore, we propose the adoption of Human Appropriation of Net Primary Production (HANPP), i.e., biomass use, as one of two metrics when assessing human impacts on biodiversity.”
Advocating for Enhanced Global Models
As we face an escalating series of potentially dire risks at the global level, it’s crucial that our developmental strategies align with scientific benchmarks. This has been exemplified by the Paris Agreement’s commitment to restrain global temperature rises to 1.5°C. Similarly, the international consensus during the 2022 Montreal-Kunming COP15 was to arrest and reverse the degradation of biodiversity both terrestrially and marine-wise, according to Johan Rockström.
“Our study shows, however, that this is by far not enough. The Planetary Boundaries science provides a ‘guide for action’ if we truly want to secure prosperity and equity for all on Earth, and this goes well beyond climate only, requiring novel Earth system modelling and analysis, and systematic efforts to protect, recover and rebuild planetary resilience.”
Katherine Richardson concludes, “This new study will serve as a wake-up call for many and increase focus in the international community on the necessity of limiting our impacts on the planet in order to preserve and protect the Earth conditions that allow advanced human societies to flourish.”
Image Credit: Shutterstock
