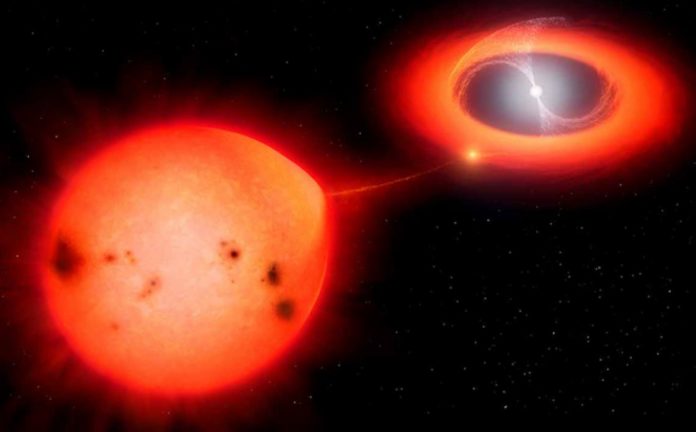
Astronomers are thrilled after witnessing the fastest nova ever recorded. The strange occurrence led astronomers’ attention to an even stranger star. They may uncover answers to not only the nova’s many perplexing characteristics, but also to wider concerns about the chemistry of our solar system, star death, and the evolution of the universe as they study it.
The study team, coordinated by Arizona State University Regents Professor Sumner Starrfield, University of Minnesota Professor Charles Woodward, and The Ohio State University Research Scientist Mark Wagner, co-authored a report published today in the American Astronomical Society’s Research Notes.
A nova is a sudden burst of bright light that comes from a pair of stars. A white dwarf – a star’s dense residual core — and a neighboring partner star are responsible for every nova. The white dwarf takes matter from its companion throughout time, which eventually falls upon the white dwarf. This material is heated by the white dwarf, which sets off a chain reaction that releases a burst of energy. The matter is shot away at high speeds by the explosion, which we see as visible light.
Over the course of a few weeks or longer, the dazzling nova normally fades. The nova V1674 Hercules exploded bright enough to be seen with the naked eye on June 12, 2021, but it faded away in just over a day. It seemed as if someone had turned on and off a flashlight.
This nova is a valuable study subject because nova events at this speed are uncommon.
“It was only about one day,” says Starrfield, an astronomer from ASU’s School of Earth and Space Exploration. “The previous fastest nova was one we studied back in 1991, V838 Herculis, which declined in about two or three days.”
While the astronomical community was watching V1674 Hercules, other researchers discovered that its speed wasn’t its only unique feature. It also emits pulsing light and energy, similar to the sound of a resounding bell.
Observers can detect a wobble every 501 seconds using both visible light and X-rays. The nova is still wobbling a year after it exploded, and it appears to have been going on for even longer. Starrfield and his colleagues have continued to look into this strange phenomenon.
“The most unusual thing is that this oscillation was seen before the outburst, but it was also evident when the nova was some 10 magnitudes brighter,” adds Wagner. “A mystery that people are trying to wrestle with is what’s driving this periodicity that you would see it over that range of brightness in the system.”
While monitoring the matter expelled by the nova explosion, the scientists found something strange: some form of wind is influencing the flow of material into space surrounding the system, which may be based on the locations of the white dwarf and its partner star.
Though the fastest nova is (literally) showy, it’s worth studying because novae can reveal significant details about our solar system and even the entire cosmos.
During a nova explosion, a white dwarf accumulates and modifies stuff, then seasons the surrounding space with new material. It’s a crucial aspect of the matter-in-space cycle. Novae eject elements that will eventually create new star systems. Such catastrophes also aided in the formation of our solar system, ensuring that Earth is more than a carbon blob.
Starrfield says, “we’re always trying to figure out how the solar system formed, where the chemical elements in the solar system came from.”
“One of the things that we’re going to learn from this nova is, for example, how much lithium was produced by this explosion. We’re fairly sure now that a significant fraction of the lithium that we have on the Earth was produced by these kinds of explosions.”
Because a white dwarf star doesn’t always lose all of its accumulated materials during a nova explosion, it accumulates mass with each cycle. This would eventually make it unstable, and the white dwarf could cause a type 1a supernova, which is one of the brightest events in the universe. Each type 1a supernova gets to the same level of brightness, so they are called “standard candles.”
“Standard candles are so bright that we can see them at great distances across the universe. By looking at how the brightness of light changes, we can ask questions about how the universe is accelerating or about the overall three-dimensional structure of the universe ,” Woodward adds.
“This is one of the interesting reasons that we study some of these systems.”
Furthermore, novae can reveal more about how stars in binary systems die, a process that is yet poorly understood. They also serve as living labs, allowing scientists to observe nuclear physics in action while also putting theoretical concepts to the test.
Astronomers were surprised by the nova. It wasn’t noticed by scientists until Seidji Ueda, a Japanese amateur astronomer, spotted and reported it.
Citizen scientists, like contemporary technology, are becoming increasingly significant in the study of astronomy. The team is still able to monitor the nova thanks to the Large Binocular Telescope’s wide aperture and other observatory equipment, including its pair of multi-object double spectrographs and exceptional PEPSI high-resolution spectrograph, even though it is now too faint for other types of telescopes to see.
They intend to look into the cause of the outburst and the processes that led to it, as well as the explanation for the outburst’s record-breaking decrease, the forces that caused the observed wind, and the cause of the pulsating brilliance.
Image Credit: MARK GARLICK
You were reading: Amateur Astronomer Spots Weird Star Producing Fastest Nova Ever Seen