Over a vast section of the Milky Way’s disc, we can now see how the objects travel.
Radial velocity
The third Gaia data release reveals the velocity at which over 30 million objects in the Milky Way (mainly stars) travel toward or away from us. This is referred to as ‘radial velocity.’ Over a vast section of the Milky Way’s disc, we can now see how the objects travel.
The bright spots (moving away from us) and dark spots (moving toward us) show that the disc is moving along the line of sight (moving toward us). By contrast, you can see several objects whose radial speed is different from that of their immediate surroundings.
The LMC and SMC (Large and Small Magellanic Clouds) can be seen in the image’s lower right corner as bright dots. The Sagittarius dwarf galaxy can be seen as a faint, almost vertical stripe below the center of the Milky Way. Several globular clusters, such as 47 Tucanae, the black dot to the left of the SMC, appear as tiny dots in the image.
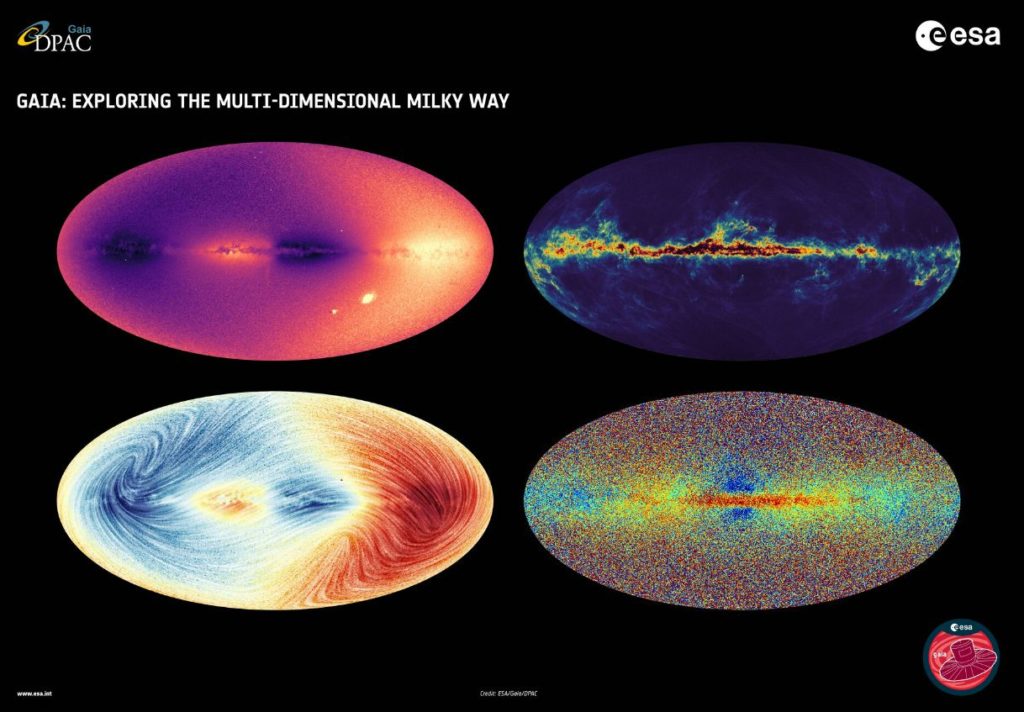
Proper motion and radial velocity
This sky map depicts the Milky Way’s velocity field for 26 million stars. The colors represent the line-of-sight radial velocities of stars. The portions of the sky where the average motion of stars is towards us are shown in blue, while the regions where the average motion is away from us are shown in red. The lines in the illustration depict the motion of stars projected on the sky (proper motion). These graphs show how galactic latitude and longitude affect the direction of stellar speed. This image does not include the Large and Small Magellanic Clouds (LMC and SMC) because only stars with well-defined distances were used.
Dust from interstellar space
Gaia not only catalogs our galaxy’s stars, but also tells us what lies beyond them. The space between stars is not empty; instead, it is densely packed with dust and gas clouds, from which stars emerge.
These maps give us crucial information on the physical mechanisms that lead to the development of stars, galaxies, and our own galaxy’s history.
This image depicts the Milky Way’s interstellar dust. The black patches in the Galactic plane’s center are locations with a lot of interstellar dust, which fade to yellow as the amount of dust decreases. There is very little dust in the dark blue regions above and below the Galactic plane.

Chemical chart
The composition of stars can reveal their birthplace and subsequent journey, and hence the history of the Milky Way. Gaia is delivering us a chemical map of the cosmos with today’s data release.
We can observe that certain stars in our galaxy are comprised of primordial material, while others, such as our Sun, are made of stuff enriched by past generations of stars, thanks to Gaia. Metals are more abundant in stars closer to the galaxy’s center and plane than in stars farther away.
This all-sky picture from Gaia’s data release 3 displays a sampling of Milky Way stars. The metallicity of the stars is indicated by the color. Metals are more abundant in redder stars.
Image Credit: ESA
You were reading: This new sky map shows the Milky Way in motion