Dr. David Heymann, former head of WHO’s emergency department, believes sexual misconduct at two European parties was the main source of the monkeypox outbreak.
While the world watches for monkeypox to become the next pandemic, one of the World Health Organization’s top advisers has suggested an explanation for the rare disease’s surprising breakout in wealthy countries in recent weeks.
Dr. David Heymann, the former chief of the World Health Organization’s emergency department, told the Associated Press in an exclusive interview that sexual transmission among gay and bisexual males at two raves in Spain and Belgium was the most likely cause of the monkeypox outbreak.
“We know monkeypox can spread when there is close contact with the lesions of someone who is infected, and it looks like sexual contact has now amplified that transmission,” Heymann told the Associated Press.
Dr. Susan Hopkins of the UK Health Security Agency confirmed with Heymann’s claim, telling the BBC that a large number of recent cases in the UK and Europe had been gay and bisexual men. The illness is not tied to sexual preference or limited to homosexual men.
Monkeypox has been reported in more than a dozen countries, including Canada, Spain, Israel, France, Switzerland, the United States, and Australia
On Monday, health officials in the United States confirmed one case in Massachusetts and four probable cases in Utah, Florida, and New York City. All of the males had traveled outside of the United States.
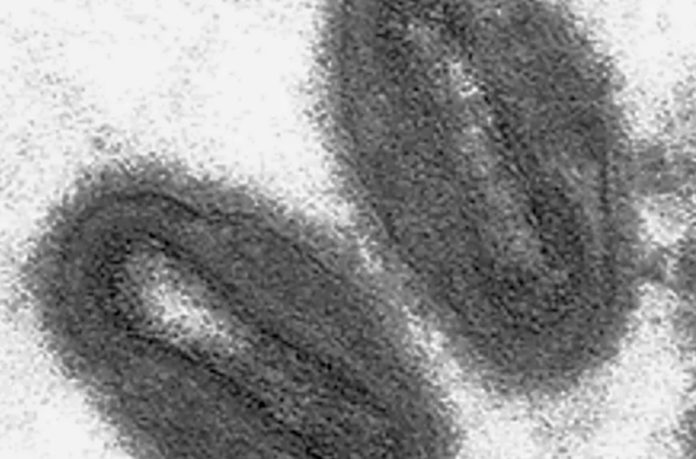
Moneypox is mostly found in animals. It’s a zoonotic disease caused by the monkeypox virus, which can infect both animals and humans. In the 1950s, the virus was discovered in monkeys, and the first human case was verified in 1970.
However, cases have been reported in the UK this year after a British citizen returned from a vacation to Nigeria. It began to spread farther after that. It is now found in countries all over the world, with the majority of them in Western Europe.
Although the disease can be fatal, with a fatality rate of roughly 10% in the worst instances, it is usually moderate.
Monkeypox is a lesser variation of smallpox, despite the fact that it is connected to the deadly disease.
Monkeypox causes skin lesions, rashes, and blisters in the same way that smallpox does.
The disease also exhibits flu-like symptoms, which usually appear first, such as lethargy, back pain, muscular aches, fever, severe headaches, and lymph node swelling, which the WHO states is a specific feature of monkeypox.
This initial invasion lasts only a few days, and the skin eruptions appear 1-3 days after the fever has passed.
These skin eruptions mainly affect the face, but they can also affect the palms of the hands, soles of the feet, eyes, and genitals.
Monkeypox does not have a specific therapy or vaccine. The smallpox vaccine is the most effective prophylactic measure. After smallpox was eradicated in the United States and most of the world in 1972, routine vaccination of the general public in the United States ended, leaving persons under the age of 40 vulnerable.
Image Credit: Getty
You were reading: This is the Most Likely Source of Monkeypox Spread, According to Experts